PARAMOUNT SCHOOL SYSTEM
Subject: Chemistry – I
Unit 5: Chemical Bonding
Why do atoms react?
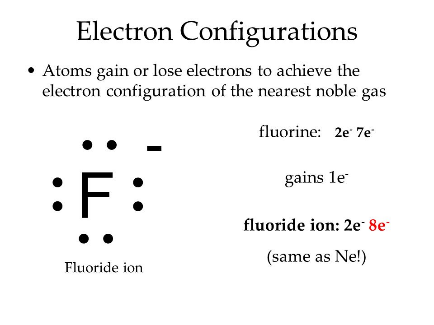
Atoms, except the noble gases, tend to react with other elements. They do this to become more stable by losing, gaining, or sharing electrons. By doing so, they achieve the same electron configuration as the nearest noble gas, which makes them stable.
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 5.1
1. Describe the formation of cations for the following metal atoms.
(a) Li (atomic no. 3)
Lithium belongs to Group IA. It has one electron in the valence shell. Lithium loses one electron to complete noble gas electronic configuration.
Li: 1s2 2s1 Li+ 1s2
We can also represent this by electron dot structure.

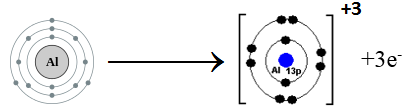
(b) Al (atomic no.13)
Aluminum belongs to Group III A. It has three electrons in the valence shell. Aluminum loses three electrons to complete noble gas electronic configuration.
Al: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1 Al+3 1s2 2s2 2p6
We can also represent this by electron dot structure.
2. Represent the formation of cations for the following metal atoms using electron dot structures.
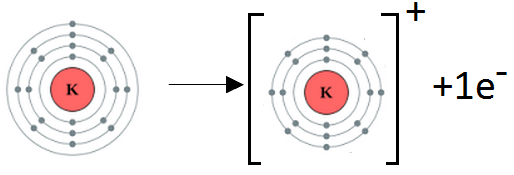
(a) Formation of K+ ion:
Potassium belongs to Group I A. It has one electron in the valence shell. Potassium loses one electron to complete noble gas electronic configuration.
K: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p64s1 K+1 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
We can also represent this by electron dot structure.
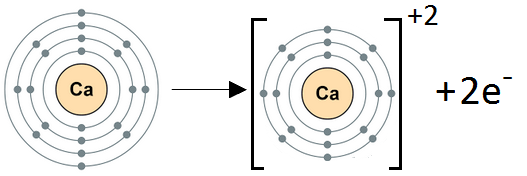
(b) Formation of Ca+2 ion:
Calcium (Ca) belongs to Group IIA. It has two electrons in its valence shell. Calcium loses two electrons to achieve the noble gas electronic configuration.
Ca: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p64s2 Ca+2 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
We can also represent this by electron dot structure.
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 5.2
1. Describe the formation of anions by the following non-metals
(a) Sulphur (atomic No. 16)
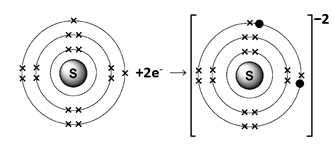
Sulfur (S) belongs to Group VIA. It has six electrons in its valence shell. Sulfur gains two electrons to complete its noble gas electronic configuration.
S: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4 +2e– → S-2 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
We can also represent this by electron dot structure.
(b) Chlorine (atomic No. 17)
Chlorine (Cl) belongs to Group VIIA. It has seven electrons in its valence shell. Chlorine gains one electron to complete its noble gas electronic configuration.
Cl: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5+1ē Cl-1 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
We can also represent this by electron dot structure.
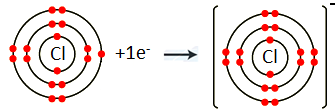
2. Represent the formation of anions by the following non-metals using electron dot structures.
(a) N:
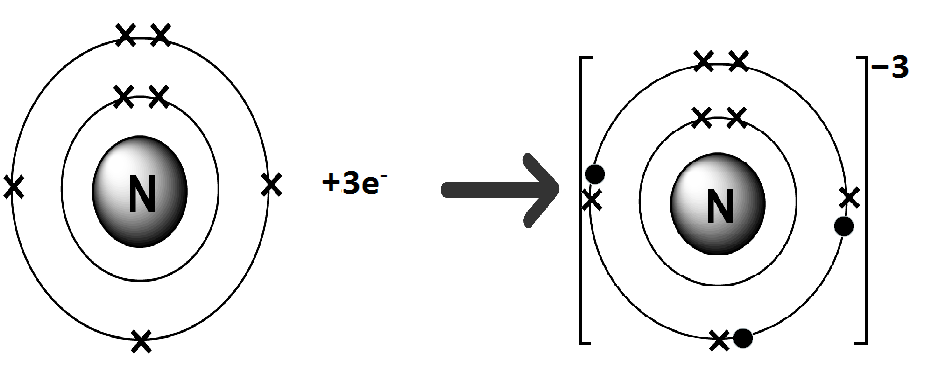
Nitrogen (N) belongs to Group VA. It has five electrons in its valence shell. Nitrogen gains three electrons to complete its noble gas electronic configuration.
N: 1s2 2s2 2p3 +3e– → N-3 1s2 2s2 2p6
We can also represent this by electron dot structure.
(b) P:
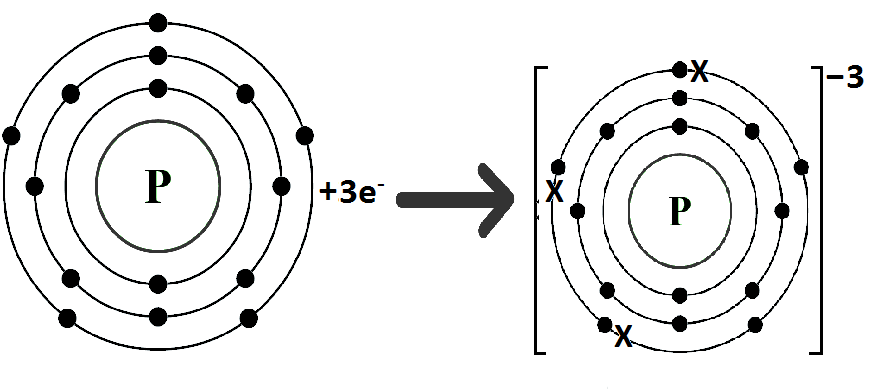
Phosphorus (P) belongs to Group VA. It has five electrons in its valence shell. Phosphorus gains three electrons to complete its noble gas electronic configuration.
P: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3+3ē P-3 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
We can also represent this by electron dot structure.
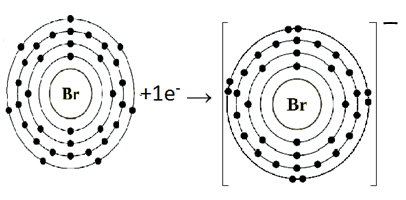
(c) Br:
Bromine (Br) belongs to Group VIIA. It has seven electrons in its valence shell. Bromine gains one electron to complete its noble gas electronic configuration.
Br: 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p5 +e– → Br-1 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p6
We can also represent this by electron dot structure.
(d) H:
Hydrogen (H) belongs to Group IA. It has one electron in its valence shell. Hydrogen can gain one electron to complete its noble gas electronic configuration.
H: 1s1 +1ē H-1 1s2
We can also represent this by electron dot structure.
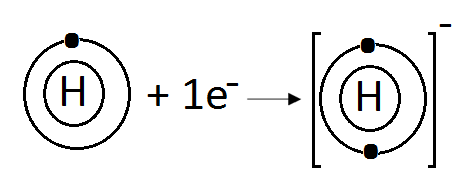
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 5.3
For each of the following pair of atoms, use electron dot and electron cross structures to write the equation for the formation of ionic compound.
- Mg and O
Mg is metal and O is non-metal. Metal atom tends to lose electrons and non-metal atoms tends to gain electrons to complete its noble gas electronic configuration. Mg atom has two electrons in its outermost shell. It loses two electrons to form Mg+2 ion. Since O atom has six electrons in outermost shell, so it gains two electrons to form O-2 ion.
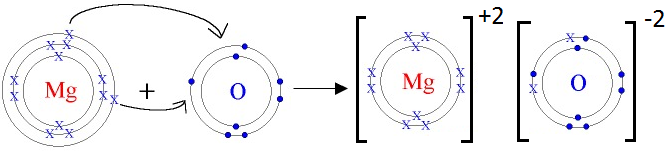
2Mg + O2 2MgO
For every Mg+2 ion we need one O-2 ion.
- Al and Cl:
Al is metal and Cl is non-metal. Metal atom tends to lose electrons and non-metal atoms tends to gain electrons to complete its noble gas electronic configuration. Al atom has three electrons in its outermost shell. It loses three electrons to form Al+3 ion. Since Cl atom has seven electrons in outermost shell, so it gains one electron to form Cl– ion.
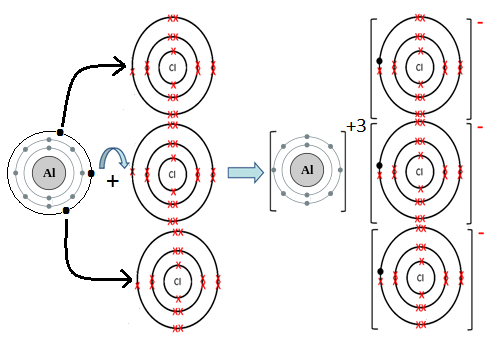
2Al + 3Cl2 → 2AlCl3
For every Al+3 ion we need one Cl– ion.
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 5.4
Recognize the following compounds as having ionic bonds.
- KCl:
K is metal and Cl is non-metal. Metal atom tends to lose electrons and non-metal atoms tends to gain electrons to complete its noble gas electronic configuration. K atom has one electron in its outermost shell. It loses one electron to form K+ ion. Since Cl atom has seven electrons in outermost shell, so it gains one electron to form Cl– ion.
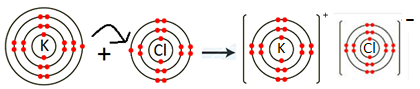
2K + Cl2 → 2KCl
For every K+ ion we need one Cl– ion.
- AlCl3:
Al is metal and Cl is non-metal. Metal atom tends to lose electrons and non-metal atoms tends to gain electrons to complete its noble gas electronic configuration. Al atom has three electrons in its outermost shell. It loses three electrons to form Al+3 ion. Since Cl atom has seven electrons in outermost shell, so it gains one electron to form Cl– ion.
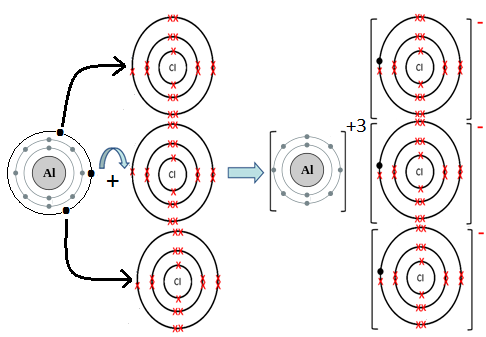
2Al + 3Cl2 → 2AlCl3
For every Al+3 ion we need three Cl– ion.
- MgF2:
Mg is metal and F is non-metal. Metal atom tends to lose electrons and non-metal atoms tends to gain electrons to complete its noble gas electronic configuration. Mg atom has two electrons in its outermost shell. It loses two electrons to form Mg+2 ion. Since F atom has seven electrons in outermost shell, so it gains one electron to form F– ion.
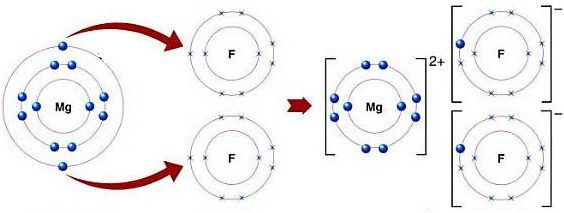
Mg + F2 → MgF2
For every Mg+2 ion we need two F– ions.
- NaF:
Na is metal and F is non-metal. Metal atom tends to lose electrons and non-metal atoms tends to gain electrons to complete its noble gas electronic configuration. Na atom has one electron in its outermost shell. It loses one electron to form Na+ ion. Since F atom has seven electrons in outermost shell, so it gains one electron to form F– ion.
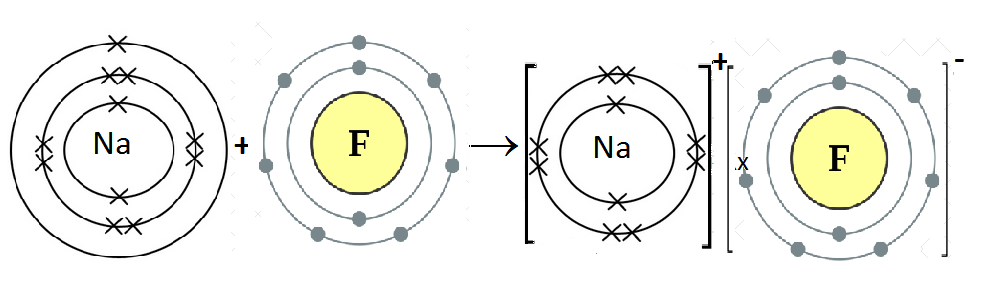
2Na + F2 → 2NaF
For every Na+ ion we need one F– ion.
- NaBr
Na is metal and Br is non-metal. Metal atom tends to lose electrons and non-metal atoms tends to gain electrons to complete its noble gas electronic configuration. Na atom has one electron in its outermost shell. It loses one electron to form Na+ ion. Since Br atom has seven electrons in outermost shell, so it gains one electron to form Br– ion.
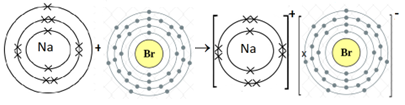
2Na + Br2 → 2NaBr
For every Na+ ion we need one Br– ion.
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 5.5
Draw electron cross and dot structures for the following molecules.
(a) NH3
N has five electrons in its valence shell and needs three electrons to complete its octet. H has only one electron and needs one electron to complete its duplet. So, N can form three single bonds with H atoms. N is the central atom.
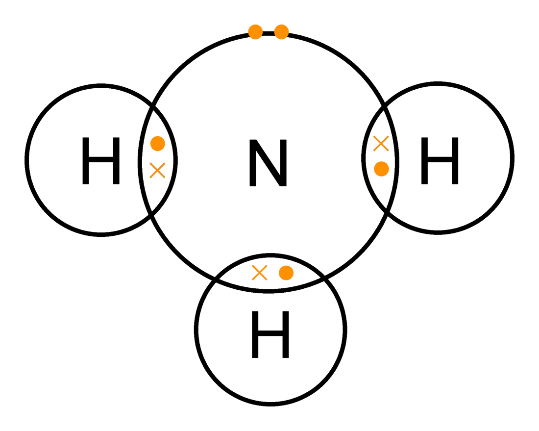 |
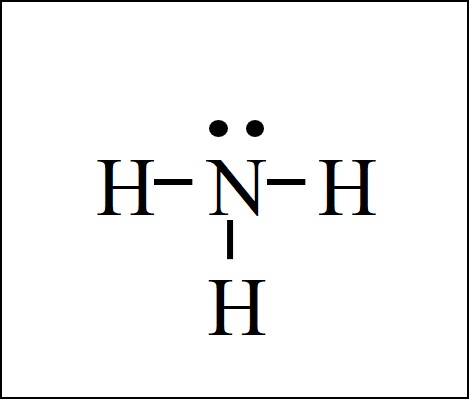 |
(b) HCl
H has one electron and needs one electron to complete its duplet. Cl has seven electrons in its valence shell and needs one electron to complete its octet. So, H can form a single bond with Cl. H is the central atom.
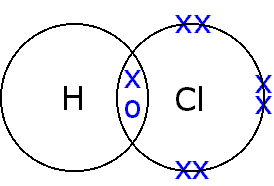 |
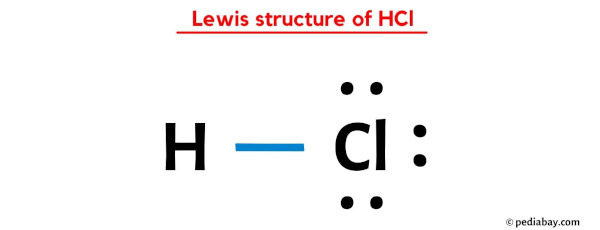 |
(c) CH3OH
C has four electrons in its valence shell and needs four electrons to complete its octet. H has one electron and needs one electron to complete its duplet. O has six electrons in its valence shell and needs two electrons to complete its octet. So, C can form three single bonds with H atoms and one single bond with O. O can form one single bond with C and one single bond with H. C is the central atom.
 |
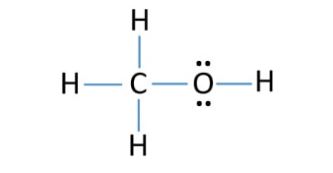 |
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 5.6
Draw electron cross and electron dot structures for the following molecules.
(a) CS2 an organic solvent that dissolves Sulphur, Phosphorus etc.
C has four electrons in its valence shell and needs four electrons to complete its octet. S has six electrons in its valence shell and needs two electrons to complete its octet. Therefore, C can form two double bonds with S. C is the central atom in the molecule.
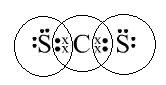 |
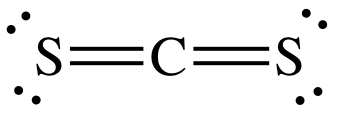 |
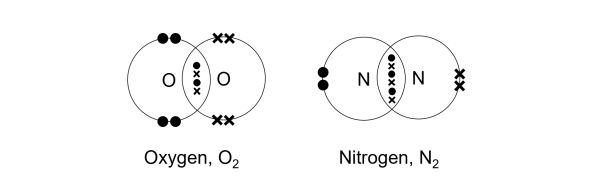
(b) N2 a component of air
Each nitrogen atom (N) has five electrons in its valence shell and requires three electrons to complete its octet. When two nitrogen atoms come together to form N₂, they share three pairs of electrons via a triple bond. Each nitrogen atom contributes three electrons to complete noble gas electronic configuration.
 |
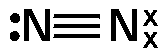 |
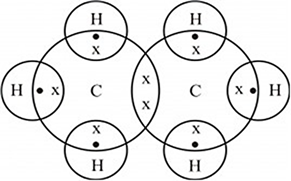
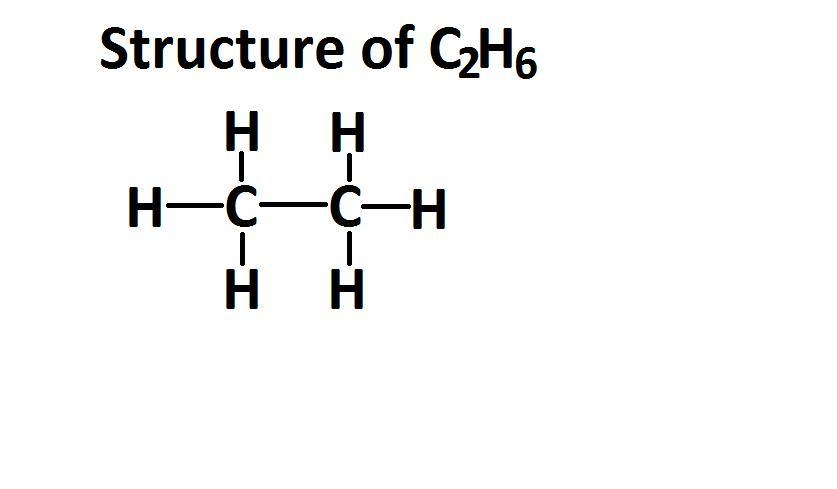
(c) C2H6, ethane a component of natural gas.
Carbon atom (C) has four electrons in its valence shell and needs four electrons to complete its octet. Hydrogen (H) has one electron and needs one electron to complete its duplet. Each carbon atom can form three single bonds with H atoms and one single bond with another C atom. Therefore, in C₂H₆, each C forms three single bonds with H and one single bond with the other C.
 |
 |
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 5.7
1. Differentiate between polar and non-polar covalent bonds.
| Non-Polar Covalent Bond | Polar Covalent Bond |
| Formed between two similar atoms. | Formed between two different atoms |
| Both atoms exert the same force on the shared electrons. | More electronegative atom pulls shared electrons more |
| No partial charges; equal electron distribution | Partial charges; more electronegative atom becomes partially negative |
| For example: H-H, O=O | For example: H₂O, NH₃, HCl |
2. How is coordinate covalent bond different from normal covalent bond?
| Normal Covalent Bond | Coordinate Covalent Bond |
| Each atom contributes one electron to the shared pair | One atom donates both electrons to the shared pair |
| Mutual attraction of both nuclei to the shared electron pair | One atom donates a pair of electrons to bond with another |
| Electrons come from both atoms | Electrons come from one atom initially |
| For Example: H₂, O₂, N₂ | For Example: NH₄⁺ (ammonium ion), [Cu(NH₃)₄]²⁺ (copper-ammonia complex) |
Review Questions
Q.1 Encircle the correct answer:
- Which of the following atoms will form an ion of charge -2?
Atomic Number Mass Number
- 12 24
- 14 28
- 8 8
- 10 20
- Which of the following atoms will not form cation or anion.
a. A (Atomic No. 16) b. B (Atomic No.. 17)
c. C (Atomic No. 18) d. D (Atomic No. 19)
- Which of the following atoms will form cation having atomic number.
a. 20 b. 18 c. 17 d. 15
- Which of the following atoms obey duplet rule?
a. O2 b. F2 c. H2 d. N2
- Silicon belongs to Group IV A. It has ____ electrons in the valence shell
a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 6
- Phosphorus belongs to third period of Group VA. How many electrons it needs to complete its valence shell.
a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 5
- In the formation of AlF3, aluminum atom loses ____ electrons.
a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4
- Which of the following is not true about the formation of Na2S:
a. Each sodium atom loses one electron b. Sodium forms cation
c. Sulphur forms anion d. Each sulphur atom gains one electron
- Identify the covalent compound
a. NaCI b. MgO c.H20 d. KF
2. Give short answers
(i) State octet and duplet rules
Octet rule:
The tendency of atoms to acquire eight electronic configurations in their outermost shell during bond formation bonding is called octet rule.
Example:
Chlorine (Cl) belongs to Group VIIA. It has seven electrons in its valence shell. Chlorine gains one electron to complete its noble gas electronic configuration.
Cl: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5+1ē Cl-1 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
We can also represent this by electron dot structure.

Duplet rule:
The tendency of atoms to acquire two electronic configurations in their outermost shell during bond formation is called duplet rule.
Example:
Hydrogen (H) belongs to Group IA. It has one electron in its valence shell. Hydrogen can gain one electron to complete its noble gas electronic configuration.
H: 1s1 +1ē H-1 1s2
We can also represent this by electron dot structure.
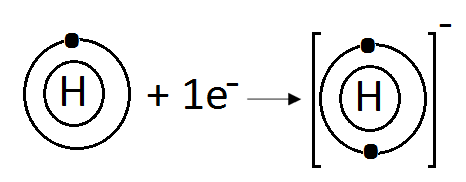
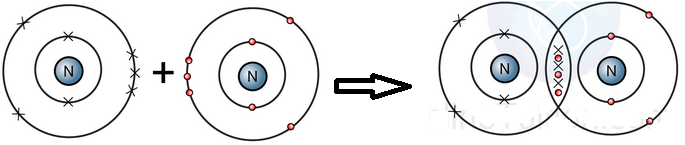
(ii) Explain formation of covalent bond between two nitrogen atoms.
Each nitrogen atom (N) has five electrons in its valence shell and requires three electrons to complete its octet. When two nitrogen atoms come together to form N₂, they share three pairs of electrons via a triple bond. Each nitrogen atom contributes three electrons to complete noble gas electronic configuration.
 |
|
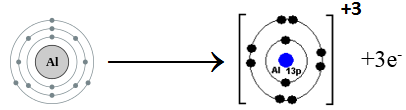
(iii) How does Al form cation?
Aluminum belongs to Group III A. It has three electrons in the valence shell. Aluminum loses three electrons to complete noble gas electronic configuration.
Al: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1 Al+3 1s2 2s2 2p6
We can also represent this by electron dot structure.
(iv) How does O form anion?
Oxygen belongs to group VIA. So it has six electrons in its valence shell. Oxygen gains two electrons to complete its noble gas electronic configuration.
O: 1s2 2s2 2p4 +2e– O-2 1s2 2s2 2p6
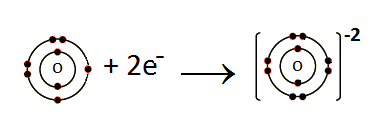
(v) Draw electron cross and dot structure for H2O molecule.
O has six electrons in its valence shell and needs two electrons to complete its octet. H has only one electron and needs one electron to complete its duplet. So, O can form two single bonds with H atoms. O is the central atom.
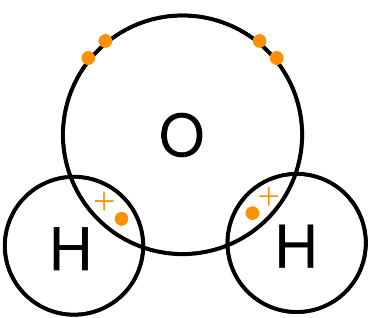 |
 |
3. Describe the importance of noble gas electronic configuration
An element that does not have two or eight electrons in its valence shell is unstable. It achieves stability by losing, gaining, or sharing electrons to complete a noble gas electronic configuration.
4. Explain how elements attain stability.
Elements attain stability by completing a duplet or octet. Atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve noble gas electronic configuration and become stable.
5. Describe the ways in which bonds may be formed?
There are two main ways:
- Ionic Bond:
An ionic bond is a strong electrostatic attraction between positively charged metal ions and negatively charged non-metal ions. Compounds that consist of ions joined by electrostatic forces are called ionic compounds.
Example:
Mg is metal and O is non-metal. Metal atom tends to lose electrons and non-metal atoms tends to gain electrons to complete its noble gas electronic configuration. Mg atom has two electrons in its outermost shell. It loses two electrons to form Mg+2 ion. Since O atom has six electrons in outermost shell, so it gains two electrons to form O-2 ion.
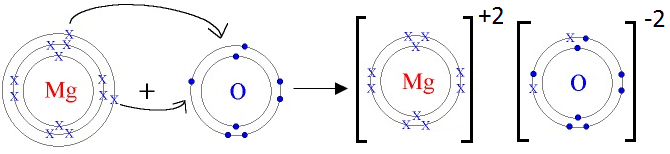
2Mg + O2 2MgO
For every Mg+2 ion we need one O-2 ion.
- Covalent Bond:
A covalent bond is formed by mutual sharing of electrons between two atoms.
Example:
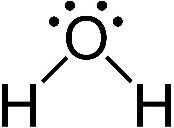
O has six electrons in its valence shell and needs two electrons to complete its octet. H has only one electron and needs one electron to complete its duplet. So, O can form two single bonds with H atoms. O is the central atom.
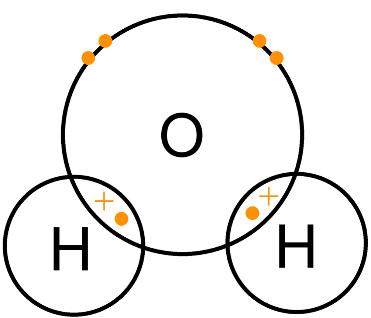 |
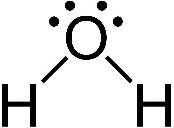 |
6. Describe the formation of covalent between two non-metallic elements.
Ans. Consider the formation of covalent bond in hydrogen molecule. A hydrogen atom has a single valence electron. Two hydrogen atoms share their valence electron to form diatomic molecule.
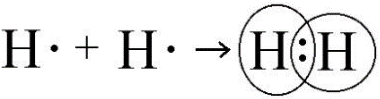 |
H + H H : H |
7. Explain with examples single, double and triple covalent bond.
Ans: Single Covalent Bond:
Covalent bond that is formed by the sharing of one electron pair is called single covalent bond.
Example:
Consider the formation of covalent bond in hydrogen molecule. A hydrogen atom has single valence electron. Two hydrogen atom share their valence electrons to form a diatomic molecule.
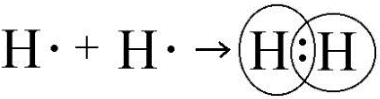
Double Covalent Bond:
Double covalent bonds are formed by sharing of two electron pairs.
Examples:
Each oxygen atom (O) has six electrons in its valence shell and requires two electrons to complete its octet. When two oxygen atoms come together to form O₂, they share two pairs of electrons via a double bond. Each oxygen atom contributes two electrons to complete the noble gas electronic configuration.
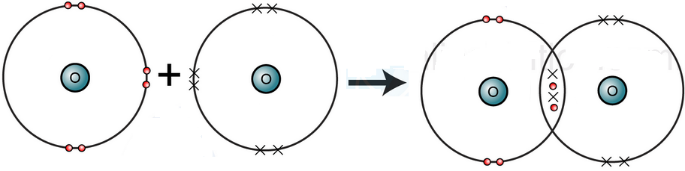 |
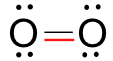 |
Triple Covalent Bond
Triple covalent bonds are formed by sharing of three electrons pairs.
Examples:
Each nitrogen atom (N) has five electrons in its valence shell and requires three electrons to complete its octet. When two nitrogen atoms come together to form N₂, they share three pairs of electrons via a triple bond. Each nitrogen atom contributes three electrons to complete noble gas electronic configuration.
 |
|
8. Find the number of valence electrons in the following atoms using the periodic table.
The number of valence electrons is the same as the group number.
Element Group Valence electrons
(a) Boron III A 3
(b) Neon VIII A 8
(c) Rubidium I A 1
(d) Barium II A 2
(e) Arsenic VA 5
9. Represent the formation of cations for the following metal atoms using electron dot structures.
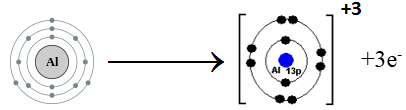
(a) Al (atomic number = 13)
Aluminum belongs to Group III A. It has three electrons in the valence shell. Aluminum loses three electrons to complete noble gas electronic configuration.
Al: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1 Al+3 1s2 2s2 2p6
We can also represent this by electron dot structure.
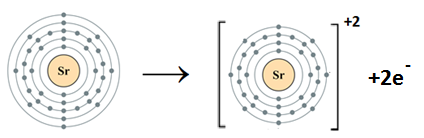
- Sr (atomic number = 18)
Strontium belongs to Group II A. It has two electrons in the valence shell. Strontium loses two electrons to complete the noble gas electronic configuration.
Sr: 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p65s2 Sr+2 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p6
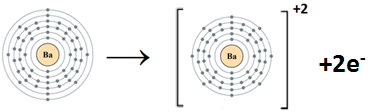
- Ba (atomic number = 56)
Ba belongs to Group II A. It has two electrons in the valence shell. Sr loses two electrons to complete the noble gas electronic configuration.
Ba:1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d105s25p66s2Ba+2 :1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d105s25p6
10. A sample of sulphur from a volcano was analyzed to give the following composition of isotopes (Atomic number of S = 16)
| Isotope | Abundance (%) |
| S-32 | 95.02 |
| S-33 | 0.76 |
| S-34 | 4.22 |
(a) Define the term isotope:
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
(b) Define the term relative atomic mass.
The mass of an atom of an element relative to the mass of an atom of C – 12 is called its relative atomic mass.
(c) Calculate the relative atomic mass of sulphur.
(d) Complete the following table.
| Isotope | Protons | Neutrons | Electrons |
| S-32 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| S-34 | 16 | 18 | 16 |
(e) Where will you place S in the periodic table:
Sulphur is placed in Group 16 (VI A) and Period 3rd of the periodic table.
(f) How many electrons will S lose or gain to acquire a stable configuration.
Sulphur belongs to Group VI A. It has six electrons in the valence shell. Sulfur gains two electrons to complete its noble gas electronic configuration.
(g) How many atoms of S are there in 0.3 mole of sulphur?
Number of moles = 0.3
Avogadro’s number = NA = 6.022×1023
Number of atoms = Number of Moles x NA
Number of atoms = 0.3 × 6.022 × 1023
=1.8066 × 1023 atoms
11. An atom of an element has atomic number 9 and mass number 19
(a) State the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of this atom.
Number of protons = atomic number = 9
Number of neutrons = atomic mass – atomic number
= 19-9 = 10
(b) State the number of electrons in this atom
Number of electrons = Number of protons = 9
(c) Show with electron cross dot diagrams, the formation of ions in the reaction of this atom with sodium atom.
The element with atomic number 9 is fluorine (F). Fluorine belongs to Group VII A. It has seven electrons in the valence shell. Fluorine gains one electron to complete its noble gas electronic configuration.
F: 1s2 2s2 2p5 + ē F– 1s2 2s2 2p6
We can also represent this by electron dot structure.
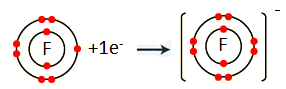 |
|
(d) Write electronic configuration of this element.
F: 1s2 2s2 2p5
(e) Point out its group in the periodic table.
Fluorine is in Group 17 (VII A) of the periodic table.
(f) Point out its period in the periodic table.
Fluorine is in Period 2nd of the periodic table.
Think Tank
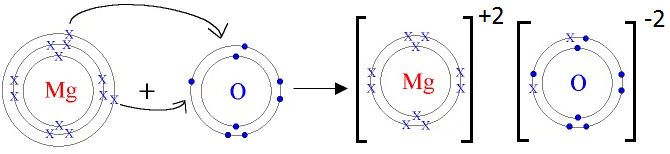
12. Magnesium oxide is a compound made up of magnesium ions and oxide ions.
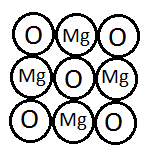
- What is the charge on these ions?
Magnesium Ion (Mg+²): +2
Oxide Ion (O–²): -2
- How these ions get these charges?
Magnesium (Mg) loses two electrons to achieve a stable noble gas configuration, forming a Mg²⁺ ion.
Oxygen (O) gains two electrons to achieve a stable noble gas configuration, forming an O–² ion.
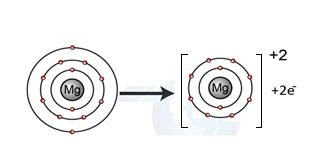
- Show with electron cross-dot diagrams the formation of these ions.
Formation of Mg+2 ion:
Mg: 1s22s22p63s2 Mg+2: 1s22s22p6
We can also represent this by electron dot structure.
Formation of O-2 ion:
O: 1s22s22p4+2e– O-2: 1s22s22p6
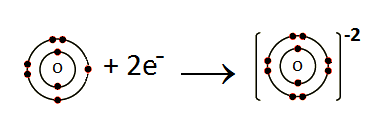
Formation of Magnesium oxide (MgO):
Mg is metal and O is non-metal. Mg atom has two electrons in its outermost shell. It loses two electrons to form Mg+2 ion. Since O atom has six electrons in outermost shell, so it gains two electrons to form O-2 ion.
For every Mg+2 ion we need one O-2 ion.
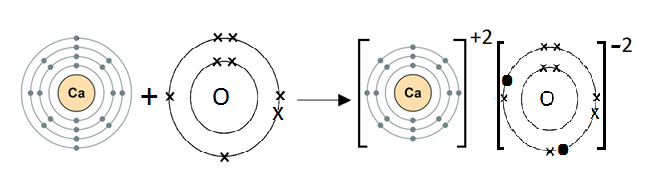
13. The diagrams below show the electronic structures of an atom of calcium and an atom of oxygen.
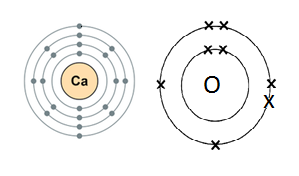
Draw structures of the ions that are formed when these atoms react.
Ca is a metal and O is a non-metal. Metal atoms tend to lose electrons, and non-metal atoms tend to gain electrons to complete their noble gas electronic configuration.
Ca atom has two electrons in its outermost shell. It loses two electrons to form a Ca+2 ion. Since O atom has six electrons in its outermost shell, it gains two electrons to form an O-2 ion.
14. The table below shows the properties of four substances.
| Substance | Melting Point | Electrical Conductivity | |
| In Solid State | In Molten State | ||
| A | High | NIL | NIL |
| B | High | NIL | Good |
| C | Low | NIL | NIL |
| D | High | Good | Good |
- Which substance is a metal?
Substance D is a metal because metal conducts electricity in solid or molten state and also has high melting points.
- Which Substance is an ionic compound?
Substance B is an ionic compound because ionic compounds do not conduct electricity in solid state but are good conductors of electricity in molten state. They also have high melting points.
- Which substance is covalent bond?
Substance C is a covalent compound because it does not conduct electricity in solid or molten state and has low melting point.
- Which substance is a non-metal?
Substance A is a non-metal which has high melting point and is non-conductor of electricity in solid or molten state.