PARAMOUNT SCHOOL SYSTEM
Subject: Chemistry – I
Unit 10: Acids, Base and Salts
Consider the following reaction.
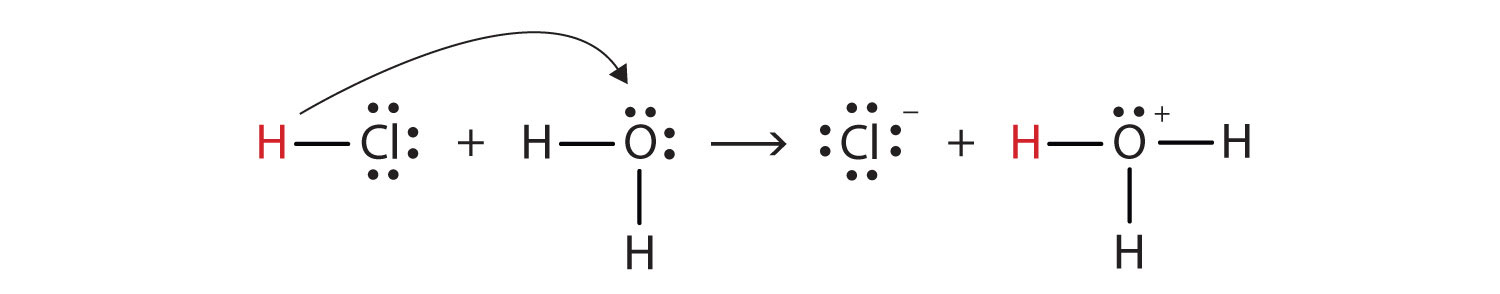
Q.1 Which substance is donating a proton?
HCl is donating a proton.
Q.2 Which substance is accepting a proton?
H₂O is accepting a proton.
Q.3 Which substance is acid?
HCl is the acid (proton donor).
Q.4 Which substance is base?
H₂O is the base (proton acceptor).
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 10.1
Identify Bronsted acids and Bronsted bases in the following reactions.
1. H₂SO₄ + H₂O ![]() HSO₄⁻ + H₃O⁺
HSO₄⁻ + H₃O⁺
H₂SO₄: Donates a proton and is converted to HSO₄⁻. Therefore, H₂SO₄ is a Bronsted acid.
H₂O: Accepts a proton and is converted to H₃O⁺. Therefore, H₂O is a Bronsted base.
2. CH₃COOH + H₂O ![]() CH₃COO⁻ + H₃O⁺
CH₃COO⁻ + H₃O⁺
CH₃COOH: Donates a proton and is converted to CH₃COO⁻. Therefore, CH₃COOH is a Bronsted acid.
H₂O: Accepts a proton from CH₃COOH and is converted to H₃O⁺. Therefore, H₂O is a Bronsted base.
3. H₂S + NH₃ ![]() NH₄⁺ + HS⁻
NH₄⁺ + HS⁻
H₂S: Donates a proton and is converted to HS⁻. Therefore, H₂S is a Bronsted acid.
NH₃: Accepts a proton and is converted to NH₄⁺. Therefore, NH₃ is a Bronsted base.
Review Questions
1. Encircle the correct answer.
- Which of the following cannot be classified as an Arrhenius acid?
(a) HNO₃ (b) H₂CO₃ (c) CO₂ (d) H₂SO₄
- Which of the following is a Bronsted base?
(a) NH₃ (b) HCl (c) CH₃COOH (d) H₂O
- Milk of magnesia contains Mg(OH)₂. It is used as an antacid. It neutralizes excess stomach acid. Which salt is formed in this reaction?
(a) MgSO₄ (b) MgCO₃ (c) MgCl₂ (d) MgO
- Ammonia is a base because it
(a) Ionizes in water to give OH⁻ ions (b) Contains OH group
(c) Can accept an electron pair (d) Can accept a proton
- Consider the following reaction: H₂O + HCl → H₃O⁺ + Cl⁻
Which species is a proton acceptor in this reaction?
(a) H₂O (b) HCl (c) H₃O⁺ (d) None
2. Give short answer.
- Write the equation for the self-ionization of water.
The reaction in which two water molecules produce ions is called as the self-ionization or auto ionization of water. Simple ionization of water can be written as:
H2O ![]()
H+ + OH–
A water molecule that loses a proton becomes a negatively charged hydroxide ion (OH-). The other water molecule which gains the proton becomes positively charged hydronium ion (H3O+). This can be written as:
2H2O ![]()
H3O+ + OH–
- Define and give examples of Arrhenius acids.
Arrhenius Acids:
An acid is a substance that ionizes in water to produce H+ ions. For example:
HCl ![]()
H+ + Cl–
H2O
HNO3 ![]()
H+ + NO3-1
Since HCl and HNO3 produce H+ ions, therefore HCl and HNO3 are acids.
- Why HCl acts as a strong acid?
HCl acts as a strong acid because it ionizes completely in aqueous solution. All the molecules of HCl dissociate in water, producing H⁺ and Cl⁻ ions. They ionize 100% in aqueous solution. This complete ionization is characteristic of strong acids
H2O
HCl ![]()
H+ + Cl–
- Why NH, acts as Bronsted-Lowry base?
According to Bronsted-Lowry theory an acid is a proton donor and a base is a proton acceptor.
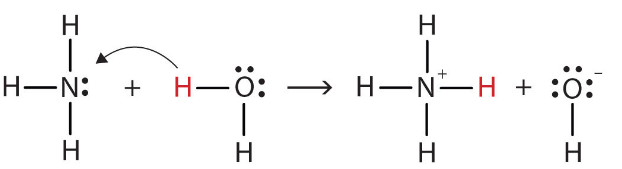
Water: Donates a proton and is converted to OH⁻. Therefore, water is a Bronsted acid.
Ammonia: Accepts a proton and is converted to NH₄⁺. Therefore, ammonia is a Bronsted base.
- Why ammonia acts as a weak base.
A base that ionizes to a little extent is called a weak base. Such bases produce fewer OH ions in aqueous solution.
Ammonia acts as a weak base because it does not ionize completely in aqueous solution. It accepts a proton from water to form ammonium ions (NH₄⁺) and hydroxide ions (OH⁻), but this ionization is not complete.
NH3 + H2O ![]()
NH4+ + OH−
3. Ammonium hydroxide and nitric acid react and produce ammonium nitrate and water. Write balanced chemical equation for this neutralization reaction.
The balanced chemical equation between ammonium hydroxide and nitric acid to form ammonium nitrate and water is.
NH4OH + HNO3 NH4NO3 + H2O
4. Write balanced chemical equations for the following neutralization reactions.
i. Sulphuric acid + Magnesium hydroxide Magnesium sulphate + water
H2SO4 + Mg(OH)2 MgSO4 + 2H2O
ii. Sulphuric acid + Sodium hydroxide Sodium sulphate + water
H2SO4 + 2NaOH Na2SO4 + 2H2O
iii. Hydrochloric acid + Calcium Hydroxide Calcium Chloride + water
2HCl + Ca(OH)2 CaCl2 + 2H2O
5. Identify Bronsted-Lowry acids or bases in the following reactions.
i. HNO3 + H2O H3O+ + NO–3
HNO₃: Donates a proton and is converted to NO₃⁻. Therefore, HNO₃ is a Bronsted acid.
H₂O: Accepts a proton and is converted to H₃O⁺. Therefore, H₂O is a Bronsted base.
ii. NH3 + HNO3 NH4NO3
HNO₃: Donates a proton and is converted to NO₃⁻. Therefore, HNO₃ is a Bronsted acid.
NH₃: Accepts the proton and forms NH₄⁺. Therefore, NH₃ is a Bronsted base.
6. Give the Bronsted-Lowry definition of an acid. Write an equation that illustrates the definition.
In 1923 J.N Bronsted and T.M Lowery independently proposed another theory to overcome the shortcomings of Arrhenius theory. According to Bronsted-Lowry theory an acid is a proton donor. For example:
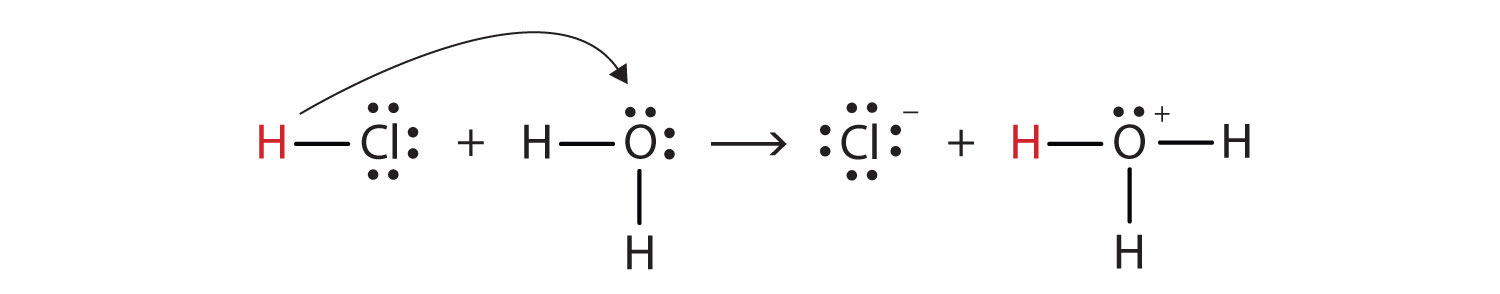
In the above reaction HCl donates proton. So HCl is an acid.
7. Identify Bronsted acids and Bronsted bases in the following reactions. Classify water as proton donor or proton acceptor.
i. CH3COOH + H2O ![]() CH3COO– + H3O+
CH3COO– + H3O+
- CH₃COOH donates a proton and becomes CH₃COO⁻, therefore CH₃COOH is an acid.
- H₂O accepts a proton and becomes H₃O⁺, therefore H₂O is a base.
ii. HCO3– + H2O ![]() CO3-2 + H3O+ (H+ and proton is same)
CO3-2 + H3O+ (H+ and proton is same)
- HCO₃⁻ donates a proton, so it is the Bronsted-Lowry acid.
- H₂O accepts a proton, so it is the Bronsted-Lowry base.
iii. NH3 + H2O ![]() NH4+ + OH–
NH4+ + OH–
- H₂O donates a proton and becomes OH⁻, so H₂O is an acid.
- NH₃ accepts the proton and becomes NH₄⁺, so it is a base.
iv. HCl + HCO3– ![]() H2CO3 + Cl–
H2CO3 + Cl–
- HCl donates a proton, so it is the Bronsted-Lowry acid.
- HCO₃⁻ accepts a proton, so it is the Bronsted-Lowry base.
v. HS– + H2O ![]() S-2 + H3O+
S-2 + H3O+
- HS⁻ donates a proton, so it is the Bronsted-Lowry acid.
- H₂O accepts a proton, so it is the Bronsted-Lowry base.
8. Classify water as proton donor and proton acceptor.
Water is amphoteric in nature. It behaves as acid as well as bese. For example,
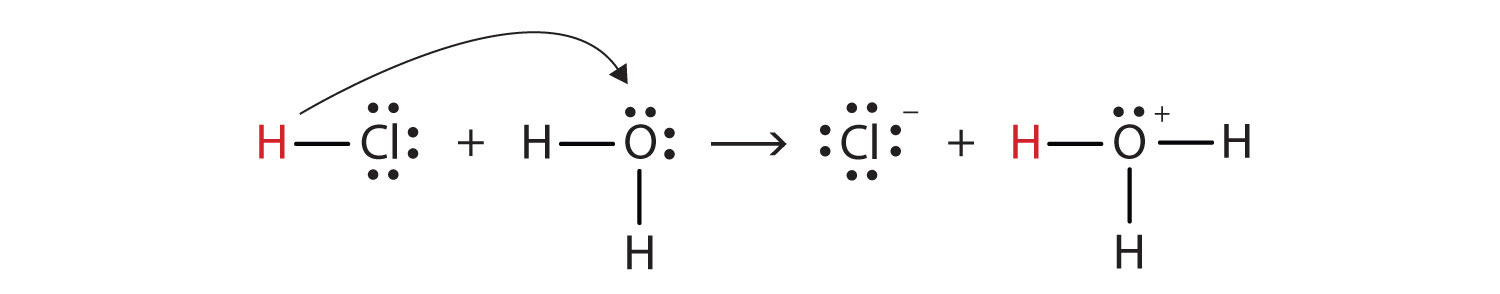
H₂O accepts a proton and becomes H₃O⁺, therefore H₂O is a base.
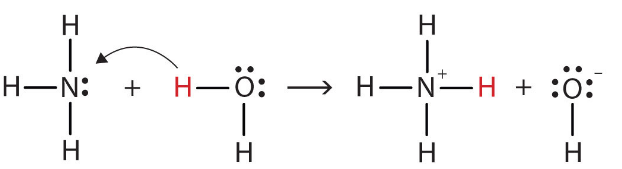
H₂O donates a proton and becomes OH⁻, therefore H₂O is an acid.
9. Write equations showing the ionization of the following as Arrhenius acids.
a. HI(aq)
HI ![]()
H+ + I–
b. HNO2 (aq)
HNO2 ![]()
H+ + NO2-1
According to Arrhenius theory an acid is a substance that ionizes in water to produce H+. So HI and HNO2 are acids.
THINK TANK
10. Compare the relative concentrations of hydrogen fons and hydroxide ions in each kind of solution?
a. acidic
In an acidic solution, the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) is greater than the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH–).
[OH–] < [H+]
b. basic
In a basic solution, the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH–)is greater than the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+).
[OH–] > [H+]
c. neutral
In a neutral solution, the concentrations of hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH–)are equal.
[OH–] = [H+]
11. Codeine, C18H21NO3 is commonly prescribed as pain killer. It dissolves in water by following reaction.
C18H21NO3 + H2O ![]() [C18H21HNO3]+ + OH–
[C18H21HNO3]+ + OH–
Differentiate Codeine and water as Bronsted-Lowry acid and base.
- C18H21NO3 accepts a proton and becomes [C18H21HNO3]+ , therefore C18H21NO3 is a base.
- H2O donates a proton and becomes OH–, therefore H2O is an acid.
12. Examine some ways in which you might determine whether a particular water solution contains an acid or a base.
Some methods to determine whether a particular water solution contains an acid or a base:
Acid:
- Acids have sour taste.
- Acids change the colour of blue litmus paper to red.
- Acids react with most metals and corrode them.
Base:
- Bases have bitter taste.
- Bases change the colour of red litmus paper to blue.
- Aqueous solution of bases has slippery touch.
