PARAMOUNT SCHOOL SYSTEM
Subject: Chemistry – I
Unit 13: Organic Chemistry
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 13.1
Write the molecular formulae of the following compounds using general formulae.
1. Alkane containing
(i) 4 carbon atoms:
Alkanes have general Formula CnH2n + 2
Butane n = 4 C4H2 x 4 + 2 = C4H10
(ii) 6 carbon atoms:
Alkanes have general Formula CnH2n + 2
Hexane n = 6 C6H2 x 6 + 2 = C6H14
2. Alkene containing
(i) 3 carbon atoms:
Alkenes have general Formula CnH2n
Propene n = 3 C3 H2 x 3 = C3 H6
(ii) 4 carbon atoms:
Alkenes have general Formula CnH2n
Butene n = 4 C4 H2 x 4 = C4 H8
3. Alkyne containing
(i) 3 carbon atoms
Alkynes have general Formula CnH2n-2
Propyne n = 3 C3 H2 x 3 – 2 = C3 H4
(ii) 4 carbon atoms
Alkynes have general Formula CnH2n-2
Butyne n = 4 C4 H2 x 4 – 2 = C4H6
4. Alcohol containing
(i) 2 carbon atoms
Alcohol have general Formula CnH2n+1 OH
Ethanol n = 2 C2 H2 x 2 + 1OH = C2H5OH
(ii) 3 carbon atoms
Alcohol have general Formula CnH2n+1 OH
Propanol n = 3 C3 H2 x 3 + 1OH = C3H7OH
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 13.2
Give the molecular, structural and condensed structural formulas for.
(a) Butane
Molecular Formula: C₄H₁₀
Structural Formula:
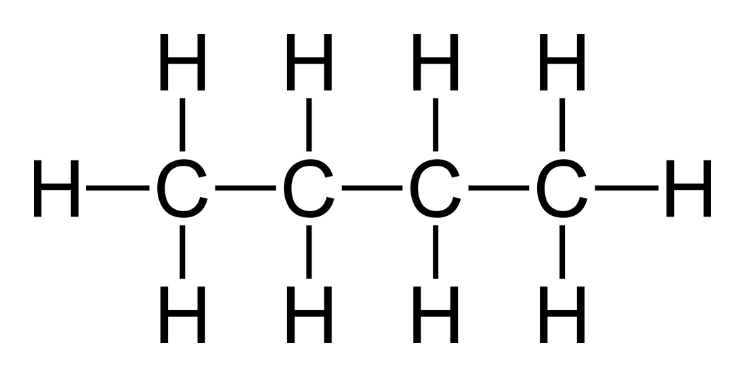
Condensed Structural Formula: CH₃-CH₂-CH₂-CH₃
(b) Hexane
Molecular Formula: C₆H₁₄
Structural Formula:
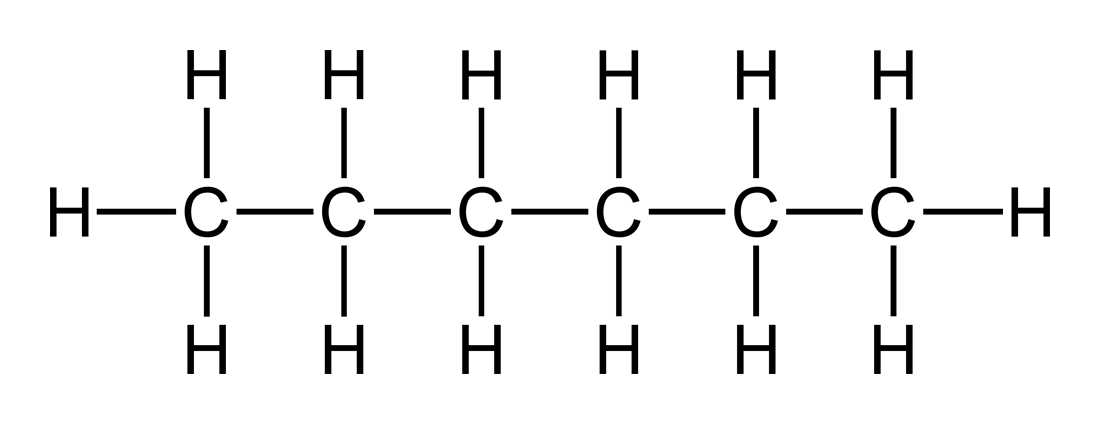
Condensed Structural Formula: CH₃-CH₂-CH₂-CH₂-CH₂-CH₃
(c) Octane
Molecular Formula: C₈H₁₈
Structural Formula:
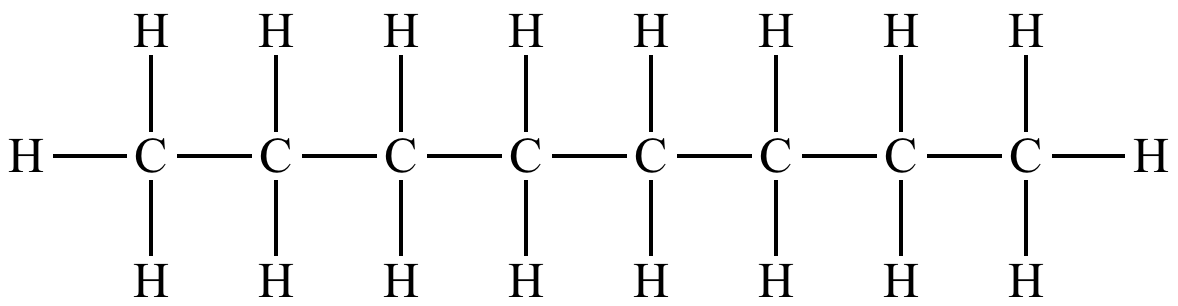
Condensed Structural Formula: CH₃-CH₂-CH₂-CH₂-CH₂-CH₂-CH₂-CH₃
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 13.3
Choose saturated and unsaturated compounds from the following.
- CH₃-CH₂-CH₂
Saturated (Alkane)
- CH3−C≡CH
Unsaturated (Alkyne)
- CH3−CH = CH2
Unsaturated (Alkene)
- CH2 = CH − CH = CH2
Unsaturated (Alkene)
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 13.4
A to E are the structural formulas of some organic compounds.
Give the letters which represents.
1. A branched chain compound.
E
2. A cyclic compound.
C
3. Two straight chain compounds.
A and D
Q. What is the difference between a carbonyl group and a carboxyl group?
| Carbonyl Group | Carboxyl Group |
| Consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom. | Consists of a carbonyl group attached to a hydroxyl group (-OH). |
| Found in aldehydes (R-CHO) and ketones (R-CO-R’). | Found in carboxylic acids (R-COOH). |
| Example:
Ethanal |
Example:
|
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 13.5
(a) CH₃CH₂OCH₂CH₃
Ether
(b) CH₃CH₂CH₂OH
Alcohol
(c) C₆H₅OH
Phenol (Because attached to benzene ring)
(d) C₂H₅OH
Alcohol
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 13.6
Identify the following compounds as an aldehyde, or a ketone or a carboxylic acid.
- CH₃COCH₂CH₃
It has a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to two carbon atoms, which makes it a ketone.
| (b) |
 |
It has a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to a hydrogen atom and a carbon chain, which makes it an aldehyde.
| (c) |
 |
It has a carboxyl group (-COOH) at the end of the carbon chain, which makes it a carboxylic acid.
REVIEW QUESTIONS
1. Encircle the correct answer.
- Condensed structural formula for butane is
(a) CH₂ – CH₂ – CH₂ (b) CH₃ – CH₂ – CH₂ – CH₃
(c) CH3 – CH₂ – CH₂ – CH₂ – CH3 (d) CH3 – CH3
- CH₃ – CH₂ – CH₃ is the chemical formula for
(a) Ethane (b) Propane (c) Butane (d) Pentane
- Which compound is not a saturated hydrocarbon?
(a) CH₃-CH₃ (b) CH₄ (c) CH₃ – CH = CH₂ (d) CH₃-CH₂-CH₃
- Stem “But” stands for how many Carbon atoms.
(a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 5
-
The functional group

is found in
(a) Alcohols (b) Ketones (c) Carboxylic acids (d) Esters
- In which of the following Compounds, oxygen is attached to two alkyl carbon atoms?
(a) Alcohol (b) Phenol (c) Ether (d) Ester
- Which of the following is an alcohol?
(a) CH₃ – CH₂ – O – CH₂ – CH₃ (b) C₃H₇OH
(c) CH₃-CH₂-COOH (d) CH₂ – CH₂ – OH
- The functional group of amines is
(a) –OH (b) – COOH (c) – NH₂ (d) – CHO
- Ethanoic acid contains the functional group
(a) –OH (b) – CO- (c) –COOH (d) – CHO
2. Give short answer.
- What is catenation?
The chemical diversity of organic compounds arises from carbon’s ability to bond with other carbon atoms to form long chains and rings. This self-linking ability is known as catenation. This property allows carbon to create a wide variety of complex organic compounds.
- Define isomerism.
Compounds having same molecular formula but different structural formula is called isomers and this process is called isomerism.
Example:
n-Butane:
CH₃-CH₂-CH₂-CH₃
iso-Butane:

- Give three examples of unsaturated compound.
Unsaturated Compounds:
Hydrocarbons containing carbon-carbon multiple bonds are called unsaturated.
| Ethene | 1-Pentene | 1-Butyne |
 |
 |
 |
- Define a functional group.
An atom or groups of atoms that give a family of organic compounds its characteristics (chemical and physical properties) is called a functional group.
Example:
Methane: CH₄
Methyl Alcohol: CH₃ – OH
Methyl Chloride: CH₃ – Cl
- What is the difference between an alkene and an alkyne?
| Alkene | Alkyne |
| Contains one or more double bonds. | Contains one or more triple bonds. |
| General Formula: C n H ₂n | General Formula: C n H ₂n – 2 |
| Example: | Example: |
| Double bond(s) between carbon atoms | Triple bond(s) between carbon atoms |
3. Identify the following compounds on the basis of functional groups they contain and encircle the functional group.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
4. What is the name of alkane having four carbon atoms in the chain?
Butane have four carbon atoms.
Molecular Formula: C₄H₁₀
Structural Formula:
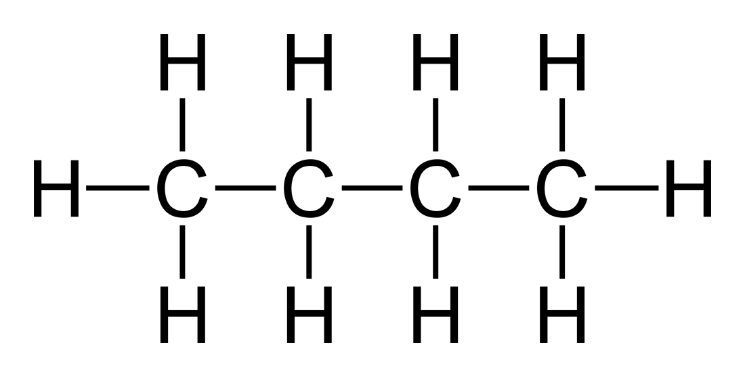
Condensed Structural Formula: CH₃-CH₂-CH₂-CH₃
5. Give the structural formula of two simple alkanes and one alkyne.
Alkanes:

Alkyne:

6. What is meant by the term functional group?
An atom or groups of atoms that give a family of organic compounds its characteristics (chemical and physical properties) is called a functional group.
Example:
Methane: CH₄
Methyl Alcohol: CH₃ – OH
Methyl Chloride: CH₃ – Cl
7. Identify following as an alcohol, aldehyde or ketone.
i. HCHO, which is used to manufacture polymers, such as urotropine which is used to treat urinary tract infection.
Aldehyde because of CHO- group is attached
ii. CH3COCH3, which is used in nail polish remover.
Ketone because of CO- group is attached.
iii. CH3CH2OH, which is used in the preparation of many organic substance such as plastics, cosmetics, tinctures etc.
Alcohol because of OH group is attached to alkyl group.
THINK TANK
8. Give molecular formula of a compound containing C, H and O and single bonds. List all the possible functional groups this compound can have?
Functional group containing Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen:
Alcohols:
Alcohols are characterized by the presence of the hydroxyl group(-OH) attached to a carbon chain.
General Formula:
![]()
Example:

Ethers:
Organic compounds that have two alkyl groups attached to the same oxygen atom are called ethers. These compounds have C – O – H linkage in their molecules.
General Formula:
![]()
Example:

9. Give the condensed structural formulas of the following compounds and classify each on the basis of functional group.
 |
 |
|
| Condensed Structural Formula |
CH3 CH2 CH2OH
(1-Propanonol) |
CH3O CH3
(Dimethyl ether) |
| Functional Group | Alcohol | Ether |
10. The diagram represents an organic compound that contains three different elements.

Select the possible compound from the following.
a. Ethanoic acid b. Propene c. Ethanol d. Propane
The compound is Ethanol.

11. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a polymer. It is used for making vinyl sheets, drainage pipes, wire insulation etc. It is obtained from vinyl chloride.

Classify Vinyl chloride as saturated or unsaturated compound.
Vinyl chloride contain double bond between two carbon atoms, so it is unsaturated hydrocarbon.
12. For each of the following, sketch the structural formulas of a two carbon compound containing the indicated functional group.
| Alcohol |
 |
| Aldehyde |
 |
| Carboxylic acid |
 |
| Alkene |
 |
13. Aspirin is a mild pain killer and fever reducer. It is manufactured from salicylic acid.

Select functional groups present in it and encircle them. Justify your selection.
Functional groups:
- Carboxyl group because two oxygen atoms are attached with a carbon atom.
- Carbonyl group because one oxygen atom is attached with carbon atom.
14. Construct the general formula for an alkane, an alkene, alkyne and an alcohol containing 4 carbon atoms.
1. Alkane containing 4 carbon atoms:
Alkanes have general Formula CnH2n + 2
Butane n = 4 C4H2 x 4 + 2 = C4H10
2. Alkene containing 4 carbon atoms:
Alkenes have general Formula CnH2n
Butene n = 4 C4 H2 x 4 = C4 H8
3. Alkyne containing 4 carbon atoms
Alkynes have general Formula CnH2n-2
Butyne n = 4 C4 H2 x 4 – 2 = C4H6
4. Alcohol containing
2 carbon atoms
Alcohol have general Formula CnH2n+1 OH
Butanol n = 4 C4 H2 x 4 + 1OH = C4H9OH
15. Water adds to ethane according to the following reaction.
![]()
Compare the functional groups in the reactant and product molecules.
In reactants:

Functional group in the reactant is alkene.
In product:

Functional group in the product is alcohol.


