Unit 3: Atomic Structure
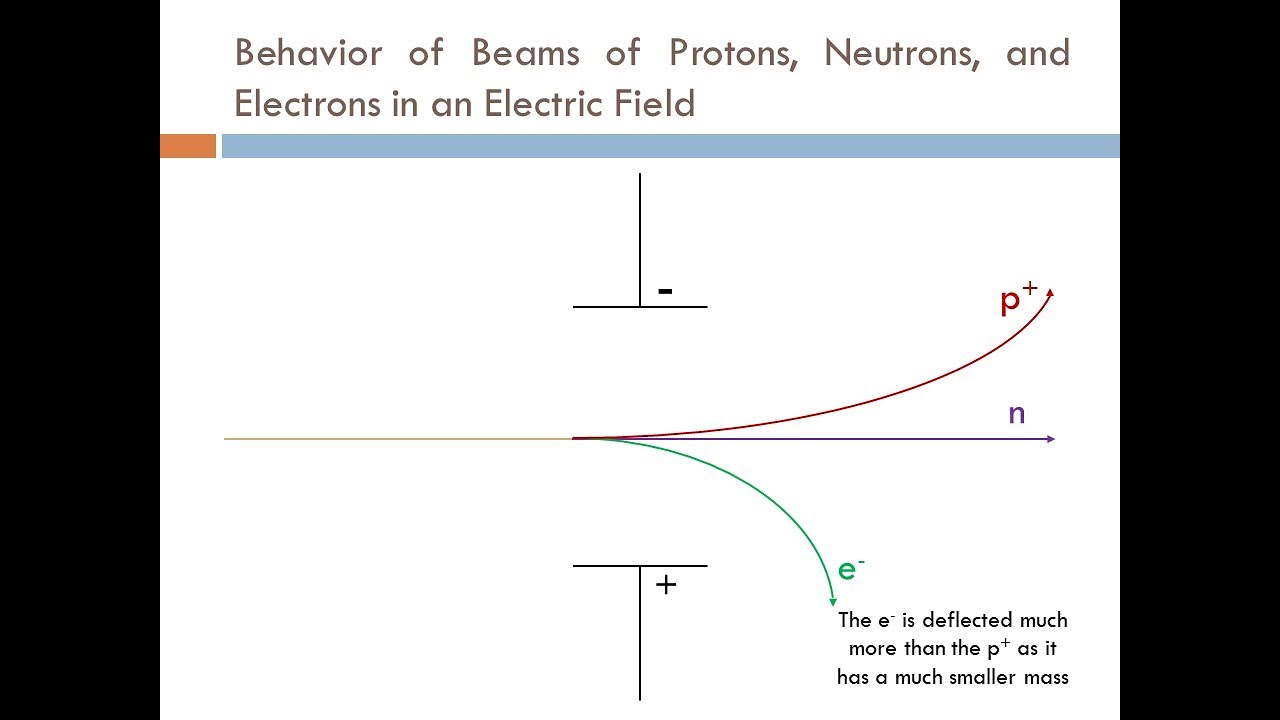
- What happens when a beam of these particles passes between two electrically charged plates?
- Protons are positively charged and are deflected on a curved path toward the negative plate.
- Electrons are negatively charged and are deflected on a curved path toward the positive plate.
- Neutrons have no charge, go straight ahead.
- If the electrons and protons are traveling at the same speed, the electrons being lighter are deflected far more strongly than the heavier protons.
- What determines the identity of an element?
The identity of an element is determined by the number of protons in its nucleus, which is also known as its atomic number.
- Do you think atomic number of He is 2?
Yes, the atomic number of helium (He) is 2. This means that a helium atom has two protons in its nucleus.
- What is the proton number of C-atom?
The proton number (or atomic number) of a carbon (C) atom is 6. This means that a carbon atom has six protons in its nucleus.
- How does the discovery of isotopes contradict Dalton’s atomic theory?
According to Dalton’s atomic theory:
“All atoms of the same element have the same mass”
Whereas isotopes are defined as:
“The atoms of an element that have same atomic number but different mass numbers”.
Which contradicted Dalton’s atomic theory.
- At what temperature would a sample of heavy water freeze?
Heavy Water freezes at 3.810C under normal atmospheric pressure.
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 3.1
An element has two isotopes A and B. The relative atomic mass of element is 35.5 amu. Relative abundance of isotope A is 75.77% and its isotopic mass is 35. Find the isotopic mass of B if its relative abundance is 24.23%.
Given:
Relative atomic mass = 35.5 amu
Abundance of isotope A = 75.77%
Abundance of isotope B = 24.23%
Isotopic mass of A = 35 amu
Isotopic mass of B = ?
To find the isotopic mass of isotope B, we can use the weighted average formula:
So, the isotopic mass of isotope B is approximately 37.06 amu.
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 3.2
Describe the formation of cations for the following metal atoms:
- Li (atomic no. 3)
Lithium belongs to Group IA. It has one electron in the valence shell. Lithium loses one electron to complete noble gas electronic configuration.
Li 1s2 2s1 Li+ 1s2
We can also represent this by electron dot structure.
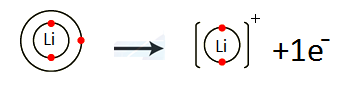
- Al (atomic no.13)
Aluminum belongs to Group III A. It has three electrons in the valence shell. Aluminum loses three electrons to complete noble gas electronic configuration.
Al 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1 Al+3 1s2 2s2 2p6
We can also represent this by electron dot structure.

CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 3.3
Describe the formation of anions by the following non-metals.
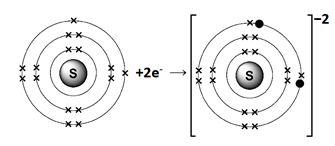
- Sulphur (atomic No. 16)
Sulphur belongs to Group VI A. It has six electrons in valence shell, it gains two electrons to complete noble gas electronic configuration.
S 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4+2ē S-2 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
We can also represent this by electron dot structure.
- Chlorine (atomic No. 17)
Chlorine belongs to Group VII A. It has seven electrons in valence shell. It gains one electron to complete noble gas electronic configuration.
Cl 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5+1ē Cl-1 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
We can also represent this by electron dot structure.
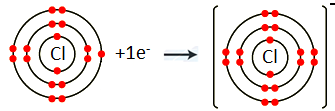
REVIEW QUESTIONS
- Encircle the correct answer.
- Chlorine has two isotopes, both of which have
(a) same mass number (b) same number of neutrons
(c) different number of protons (d) same number of electrons
- Number of neutrons in are
(a) 13 (b) 14 (c) 27 (d) 15
- Which isotope is commonly used to irradiate cancer cells?
(a) lodine-123 (b) Carbon-14 (c) Cobalt-60 (d) lodine-131
- M shell has sub-shells:
(a) 1s, 2s (b) 2s, 2p (c) 3s, 3p, 3d (d) 1s, 2s, 3s
- A sub-shell that can accommodate 6 electrons is
(a) 5 (b) d (c) p (d) f
- has electronic configuration:
(a) 1s2, 2s2, 3s1 (b) 1s2, 2s2, 2p7 (c) 1s2, 2s2, 2p5, 3s2 (d) 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s1
- Which of the following statement is not correct about isotopes?
(a) they have same atomic number (b) they have same number of protons
(c) they have same chemical properties (d) they have same physical properties
- Which isotope is used in nuclear reactors?
(a) U-234 (b) U-238 (c) U-235 (d) All of these
2. Give short answer.
- Distinguish between shell and sub-shell.
| Shell | Sub-Shell |
| Main energy levels where electrons reside | Divisions within shells where electrons are found |
| Principal quantum number (n=1, 2, 3, …) | Designated by s, p, d, f within each shell |
| Holds up to 2n² electrons | s: 2, p: 6, d: 10, f: 14 electrons |
| Higher n means higher energy level | Energy increases from s to f within a shell |
| n=2 shell | 2s and 2p sub-shells |
- Why an atom is electrically neutral?
An atom has the same number of positive protons and negative electrons which cancel each other’s effect and net charge on atom become zero. Hence atom become neutral.
- How many sub-shells are there in N shell.
The N shell corresponds to the fourth energy level of an atom. In the N shell, there are four sub-shells: s, p, d, and f.
- Give notation for sub-shells of M shell.
The M shell corresponds to the third energy level of an atom. The notation for the sub-shells in the M shell is as follows:
- 3s
- 3p
- 3d
- List the sub-shells of M Shell in order of increasing energy.
The notation for the sub-shells of the M shell in order of increasing energy is:
3s < 3p < 3d
- Can you identify an atom without knowing number of neutrons in it?
Yes, an atom can be identified by its atomic number, which equals the number of protons. Each element has a unique atomic number, defining its identity.
3. The electronic configurations listed are incorrect. Explain what mistake have been made in each and write correct electronic configurations.
X = 1s2, 2s2, 2p4 , 3p2
Y = 1s2, 2s1, 2p1
Z = 1s2, 2s2, 2p5, 3s1
According to Aufbau principle, electrons fill the lowest energy sub-shell that is available first.
1s < 2s < 2p < 3s < 3p < 4s < 3d …………
In X, 2p can accommodate 6 electrons. So correct electronic configurations is:
X = 1s2, 2s2, 2p6
In Y, 2s can accommodate 2 electrons. So correct electronic configurations is:
Y = 1s2, 2s2
In Z, 2p can accommodate 6 electrons. So correct electronic configurations is:
Z = 1s2, 2s2, 2p6
4. Which orbital in each of the following pairs is lower in energy?
(a) 2s, 2p
2s < 2p
(b) 3p, 2p
2p < 3p
(c) 3s, 4s
3s < 4s
5. Draw Bohr’s Model for the following atoms indicating the location for electron, protons and neutrons:
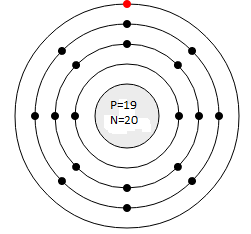
(a) Potassium (Atomic No. 19, Mass No. 39):
- Protons: 19 in the nucleus
- Neutrons: 39 −19 = 20 in the nucleus
- Electrons: 19 electrons distributed in shells
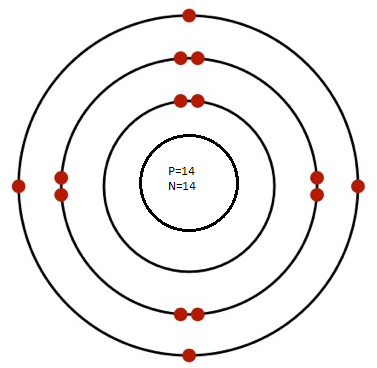
(b) Silicon (Atomic No. 14, Mass No. 28):
- Protons: 14 in the nucleus
- Neutrons: 28−14=14 in the nucleus
- Electrons: 14 electrons distributed in shells
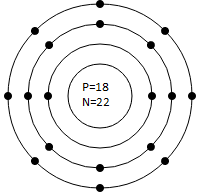
(c) Argon (Atomic No. 18, Mass No. 39):
- Protons: 18 in the nucleus
- Neutrons: 39 −18 = 21 in the nucleus
- Electrons: 18 electrons distributed in shells
6. Write electronic configuration for the following elements:
(a)
= 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p2
(b)
= 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2
(c)
= 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p1
(d)
= 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6
7. State the importance and uses of isotopes in various fields of life.
Importance and uses of isotopes in various fields of life.
- Radioactive iodine-131 is used as tracer in diagnosing thyroid problem.
- Na-24 is used to trace the flow of blood and detect possible constrictions in circulatory system.
- Iodine-123 is used to image the brain.
- Cobalt-60 is used to irradiate cancer cells.
- Carbon-14 is used to trace the path of carbon in photosynthesis.
- Radioactive isotopes are used to determine the molecular structure.
- Radioactive isotopes are used to date rocks, soils, mummies etc.
- Carbon-14 is used to estimate the age of carbon containing substance.
8. The atomic number of an element is 23 and its mass number is 56.
a. How many protons and electrons does an atom of this element have?
Since the atomic number represents the number of protons in the nucleus, the atom has 23 protons. In a neutral atom, the number of electrons equals the number of protons. Therefore, the atom also has 23 electrons.
b. How many neutrons does this atom have?
The number of neutrons can be calculated using the formula:
Neutrons (N) = Mass number (A) – Atomic number (Z)
= 56 – 23
= 33
Therefore, the atom has 33 neutrons.
9. The atomic symbol of aluminium is written as . What information do you get from it?
Atomic number = 13
Atomic mass = 27
No. of protons = No. of electrons = Atomic number=13
Number of neutrons = 27 – 13 = 14
Electronic configuration:
= 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1
Period = 3
Group = 2+1 = III A
So aluminum is metal.
