PARAMOUNT SCHOOL SYSTEM
Subject: Chemistry – I
Unit 4: Periodic Table and Periodicity of Properties
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 4.2
Identify the group and period of the following elements on the basis of electronic configurations.
(a) = 1s2 2s2 , 2p6 3s2 3p2
K L M
Valence shell is M, n = 3 so
Period = 3rd
Group = 2 + 2= 4 = IV A
(b) = 1s2 2s2 , 2p6 3s2 3p4
K L M
Valence shell is M, n = 3 so
Period = 3rd
Group = 2 + 4 = 6 = VI A
(c) = 1s2 2s2 , 2p5
K L
Valence shell is M, n = 2 so
Period = 2nd
Group = 2 + 5 = 7 = VII A
(d) = 1s2 2s2 , 2p6 3s2, 3p6
K L M
Valence shell is M, n = 3 so
Period = 3rd
Group = 2 + 6 = 8 = VIII A
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 4.3
Electronic configuration of atoms of some elements are given below. Place them into groups and periods.
P = 1s2 2s2 2p2 Q = 1s2 2s2 3p1
R = 1s2 S = 1s2 2s2
T = 1s2 2s1 W = 1s2 2s2 2p6
X = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 Y = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
Z = 1s2 2s2 2p1
|
IA |
VIIIA |
|||||||
|
IIA |
IIIA |
IVA |
VA |
VIA |
VIIA |
R |
||
|
T |
S |
Z |
P |
W |
||||
|
Q |
X |
Y |
||||||
Some elements tend to lose electrons. Why?
Elements achieve stability by completing a duplet or an octet in their outermost electron shell. Atoms lose electrons to achieve this configuration and attain stability.
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 4.4
Obtain the valence shell configuration of Al and S from their position in the periodic table.
- Aluminum (Al):
Period number of Al is 3
So, n = 3 valence shell is M
The group number is 3
So, valence electron will be present in 3s and 3p sub-shell.
Two electrons will fill 3s sub-shell and remaining one 3p sub-shell. Thus, valence shell electronic configuration is 3s2, 3p1
- Sulphur (S):
Period number of S is 3
So, n = 3 valence shell is M.
The group number is 6
So, valence electron will be present in 3s and 3p.
Two electrons will fill 3s sub-shell and remaining four 3p sub shell. Thus, valence shell electronic configuration is 3s2 3p4
Which atom has greater shielding effect Be or Mg?
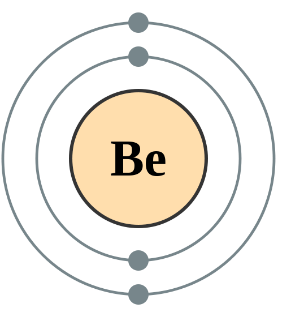
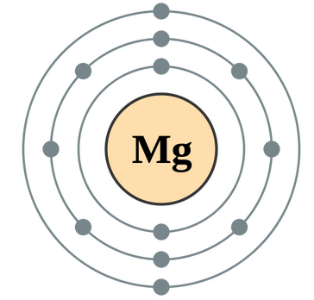
Mg have 10 inner shell electrons and Be have 2. So Mg atom will have greater shielding effect due to greater number of inner shell electrons.
Which atom has greater shielding effect Li or Be?
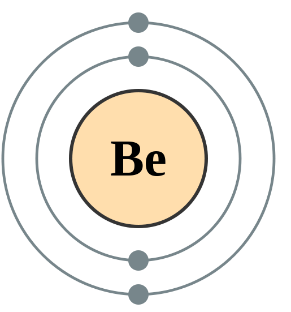
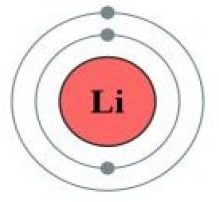
Li has two inner shell electrons and Be have also two. So, Li or Be have same shielding effect due to same number of inner shell electrons.
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 4.5
Choose the element whose atoms you expect to have smaller shielding effect.
(a) F or Cl:
F have 2 inner shell electrons and Cl have 10. So, F atom will have smaller shielding effect due to smaller number of inner shell electrons.
(b) Li or Na:
Li have 2 inner shell electrons and Na have 10. So, Li atom will have smaller shielding effect due to smaller number of inner shell electrons.
(c) B or Al:
B have 2 inner shell electrons and Al have 10. So, B atom will have smaller shielding effect due to smaller number of inner shell electrons.
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 4.6
Using the periodic table but without looking at the figure 4.4, choose the element whose atom you expect to have smaller atomic radius in each of the following pairs.
(a) O or S
As we move from top to bottom in a group atomic radius increase. Therefore, O has smaller atomic radius.
(b) O or F
As we move from left to right in a period atomic radius decrease. Therefore, F has smaller atomic radius.
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 4.7
Which atom has smaller ionization energy?
(a) B or N
Ionization energy increases from left to right in a period. Therefore, B has smaller ionization energy.
(b) Be or Mg
Ionization energy decreases from top to bottom in a group. Therefore, Mg has smaller ionization energy.
(c) C or S
Ionization energy decreases from top to bottom in a group. Therefore, Si has smaller ionization energy.
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 4.8
Which element has lower metallic character?
(a) Li or K
Metallic character increases down a group. Therefore, lithium (Li) has lower metallic character than potassium (K).
(b) Mg or Ca
Metallic character increases down a group. Therefore, magnesium (Mg) has lower metallic character than calcium (Ca).
(C) Compare and contrast ionization energy and electron affinity.
|
Ionization Energy |
Electron Affinity |
|
The minimum amount of energy required to remove the outermost electron from an isolated gaseous atom. |
The amount of energy released when an electron adds up in the valence shell of an isolated atom to form a uni-negative gaseous ion. |
|
M(g) + ionization energy → M⁺(g) + e⁻ |
X(g) + e⁻ → X⁻(g) + electron affinity |
|
Always positive (energy input is required). |
Usually negative (energy is released). |
|
Increases from left to right across a period due to increasing nuclear charge. |
Increases from left to right across a period due to increasing nuclear charge and decreasing atomic radius. |
|
Decreases from top to bottom in a group due to increasing shielding effect and atomic radius. |
Decreases from top to bottom in a group due to increasing shielding effect and atomic radius |
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 4.9
Which of the following displacement reaction will occur?
1. Cl2 (g) + 2NaF (aq) → 2NaCl (aq) + F2(g)
Will not occur because reactivity of halogens decreases down the group
F2 > Cl2
Therefore, Cl2 cannot oxidized Fe2.
2. Br2 (g) + 2KI (aq) → 2KBr (aq) + I2 (g)
Will occur because reactivity of halogens decreases down the group
Br2 > I2
Therefore, Br2 can oxidized I2.
3. I2 (g) + 2KBr (aq) → 2KI (q) + Br2 (l)
Will not occur because reactivity of halogens decreases down the group
Br2 > I2
Therefore, I2 cannot oxidized Br2.
4. Cl2 (g) + KBr (aq) → 2KCl (aq) + Br2 (l)
Will occur because the reactivity of halogens decreases down the group
Cl2 > Br2
Therefore, Cl2 can oxidized Br2.
5. Cl2 (g) + 2NaI (aq) → 2NaCl (aq) + I2 (s)
Will occur because the reactivity of halogens decreases down the group
Cl2 > I2
Therefore, Cl2 can oxidized I2.
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 4.10
Compare the general properties of metals and non-metals.
|
Metals |
Non-Metals |
||
|
High thermal conductivity; conduct heat well. |
Low thermal conductivity; poor conductors of heat. |
||
|
Good conductors of electricity due to free electrons. |
Poor conductors of electricity, with exceptions like graphite. |
||
|
Malleable and ductile; can be hammered into sheets and drawn into wires. |
Brittle; cannot be shaped easily without breaking. |
||
|
Generally, have high melting and boiling points due to strong metallic bonds. |
Generally, have lower melting and boiling points due to weaker bonds. |
REVIEW QUESTIONS
1. Encircle the correct answer.
- Number of periods in the periodic table are:
(a) 8 (b) 7 (c) 16 (d) 5
- Which of the following groups contain alkaline earth metals?
(a) IA (b) IIA (c) VIIA (d) VIIIA
- Which of the following elements belongs to VIIIA?
(a) Na (b) Mg (c) Br (d) Xe
- Main group elements are arranged in groups:
(a) 6 (b) 7 (c) 8 (d) 10
- Period number of is:
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4
- Valence shell electronic configuration of an element M (atomic no.14) is:
(a) 2s2 , 2p1 (b) 2s2 , 2p2 (c) 2s2 , 2p3 (d) 3s2 , 3p2
- Which of the following elements you expect to have greater shielding effect?
(a) Li (b) Na (c) K (d) Rb
- As you move from right to left across a period, which of the following does not increase:
(a) electron affinity (b) ionization energy
(c) nuclear charge (d) shielding effect
- All the elements of Group IIA are less reactive than alkali metals. This is because these elements have:
(a) high ionization energies (b) relatively greater atomic sizes
(c) similar electronic configuration (d) decreased nuclear charge
2. Give short answer.
- Write the valence shell electronic configuration of an element present in the 3rd period and Group ΙΙΙΑ.
The element present in 3rd period and group is aluminum. Aluminum (Al) is found in the 3rd period and Group IIIA of the periodic table so it has three valence electrons. Valence shell electronic configuration of aluminum is 3s2 3p1.
- Define halogens.
The elements in Group 17 (or Group VII-A) are called halogens. The name halogen is derived from the Greek words “halous” meaning salt and “gen” meaning former. Halogens include fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, astatine, and tennessine. Astatine and tennessine are radioactive elements with little known about their properties. All halogens are reactive non-metals and exist as diatomic molecules.
- Which atom has higher shielding effect, Li or Na?
Na have 10 inner shell electron and Li have 2. So Na atoms will have greater shielding effect due to greater number of inner shell electrons.
- Explain why, Na has higher ionization energy than K?
Na has 3 electron shells, while K has 4. Since Na is smaller in size compared to K, its valence electron is closer to the nucleus. Ionization energy decreases from top to bottom within a group, so Na has a higher ionization energy than K. - Alkali metals belong to S-block in the periodic table, why?
Alkali metals are classified in Group 1A of the periodic table, with each element having one electron in its valence shell. They belong to s-block due to their valence shell electrons occupying s-sub shells.
3. Arrange the elements in each of the following groups in order of increasing ionization energy.
(a) Li, Na, K
Ionization energy increases across a period and decreases down a group.
K < Na < Li
(b) CI, Br, I
Ionization energy increases across a period and decreases down a group.
I < Br < Cl
4. Arrange the elements in each of the following in order of decreasing shielding effect.
(a) Li, Na, K
The shielding effect increases with the addition of electron shells, so it increases down a group in the periodic table.
K > Na > Li
(b) Cl, Br, I
The shielding effect increases with the addition of electron shells, so it increases down a group in the periodic table.
I > Br > Cl
(c) Cl, Br
The shielding effect increases with the addition of electron shells, so it increases down a group in the periodic table.
Br > Cl
5. Specify which of the following elements you would expect to have the greatest electron affinity. S, P, CI
Electron affinity increases from left to right in a period so electron affinity of Cl is greater than S and P.
6. Electronic configuration of some elements are given below, group the elements in pairs that would represent similar chemical properties.
A = 1s2 2s2
B = 1s2 2s2 2p6
C = 1s2 2s2 2p3
D = 1s2
E = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3
F = 1s2 2s1
G = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1
H = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2
Elements having similar electronic configuration in their outer shells have similar chemical properties so
F = G, A = H, C = E, D = B
7. Arrange the elements in groups and periods in Q. No. 6.
|
IA |
VIIIA |
|||||||
|
IIA |
IIIA |
IVA |
VA |
VIA |
VIIA |
D |
||
|
F |
A |
C |
B |
|||||
|
G |
H |
F |
||||||
8. For normal elements, the number of valence electrons of an element is equal to the group number. Find the group number of the following elements.
, , ,
= 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1
Group number = 2 + 1 = III A
= 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4
Group Number = 2 + 4 = VI A
= 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4 4s1
Group Number = 1 = I A
= 1s2 2s2 2p4
Group Number = 2 + 4 = VI A
9. Write the valence shell electronic configuration for the following groups:
a. Alkali metals
Alkali metals belong to Group IA and have a valence shell electronic configuration of ns1, where n represents the period number.
b. Alkaline earth metals
Alkaline earth metals belong to Group IIA and have a valence shell electronic configuration of ns2, where n represents the period number.
c. Halogens
Halogens belong to Group VIIA and have a valence shell electronic configuration of ns2np5 where n represents the period number.
d. Noble gases
Noble gases belong to Group VIIIA and have a valence shell electronic configuration of (except helium) ns2 np6, where n represents the period number.
10. Write electron dot symbols for an atom of the following elements
(a) Be (b) K (c) N (d) I
(a) (b) (c) (d)

11. Write the valence shell electronic configuration of the atoms of the following elements.
(a) An element present in period 3 of Group VA
3s2 3p3
(b) An element present in period 2 of Group VI A
2s2 2p4
12. Copy and complete the following table:
|
Atomic number |
Mass number |
No. of Protons |
No. of Neutrons |
No. of electrons |
|
11 |
23 |
11 |
12 |
11 |
|
14 |
29 |
14 |
15 |
14 |
|
22 |
47 |
22 |
25 |
22 |
|
13 |
27 |
13 |
14 |
13 |
13. In which block, group and period in the periodic table where would you place each of the following elements with the following electronic configuration?
|
Block |
Group |
Period |
||
|
a. |
1s2 2s2 |
s |
IA |
2 |
|
b. |
1s2 2s2 2p5 |
p |
VIIA |
2 |
|
c. |
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 |
s |
IIA |
3 |
|
d. |
1s2 |
s |
VIIIA |
1 |
THINK TANK
14. What types of elements have the highest ionization energies and what types of elements have the lowest ionization energies?
Noble gases have the highest ionization energies because their outermost shells are complete. Alkali metals have the lowest ionization energies due to their larger atomic size.
15 (1). Two atoms have electronic configuration 1s22s22p6 and 1s22s22p63s1. The ionization energy of one is 20801KJ/mole and that of the other is 496KJ/mole. Match each ionization energy with one of the given electronic configurations. Give reason for your choice.
The first atom with the electronic configuration 1s22s22p6 has an ionization energy of 2080 kJ/mol because it corresponds to a noble gas configuration. Noble gases have high ionization energies due to their stable, complete outer electron shells.
The second atom with the electronic configuration 1s22s22p63s1 has an ionization energy of 496 kJ/mol because it is an alkali metal. Alkali metals, belonging to Group 1A, have low ionization energies due to their larger atomic size.
15(2). Use the second member of each group IA, IIA and VIIA to show that the number of valence electrons of an atom of the element is the same as its group number.
|
Group |
Element |
Valence Shell Configuration |
Valence Electrons |
|
IA |
Li |
2s1 |
1 |
|
IIA |
Mg |
3s2 |
2 |
|
VIIA |
Cl |
3s23p5 |
2+5=7 |
15(3). Letter A, B, C, D, E, F indicates elements in the following figure:
|
C |
||||||||
|
A |
B |
|||||||
|
D |
E |
|||||||
|
F |
||||||||
a. Which elements are in the same periods?
Elements A, B and D, E are in the same periods.
b. Write valence shell electronic configuration of element D.
Element D lies in Group IIA and 4th period, so electronic configuration is 4s2
c. Which elements are metals?
Elements A and D are metals
d. Which element can lose two electrons?
Element D can lose two electrons, because there are two electrons in its outermost shell
e. In which group, E is present?
Element E is present in Group VA
f. Which of the element is halogen?
Element F is halogen because group VIIA elements are known as halogens.
g. Which element will form dipositve cation?
The element D will form dipositive cation because it is in group IIA and can lose two electrons.
h. Write electronic configuration of element E.
The element E is in group VA and 4th period, so electronic configuration is 4s24p3
i. Which two elements can form ionic bond?
Elements A, F and D, C can form ionic bond.
j. Can element C form C2 molecule?
Yes, element C can form C2 molecule.
k. Which element can form covalent bonds?
Element C and F can form covalent bonds.
l. Is element F a metal or non-metal?
The element F is a non-metal.
16. Electronic configurations of four elements are given below:
- 1s22s1
- 1s22s22p5
- 1s22s22p63s2
- 1s2
Which of these elements is.
- An alkali metal
Element “a” is alkali metal because it is in group IA. Group IA elements are known as alkali metals.
- An alkaline earth metal
Element “c” is alkaline earth metal because it is in group IIA. Group IIA elements are known alkaline earth metals.
- A noble gas
Element “d” is noble gas because it is in group VIIIA. Group VIIIA elements are known as noble gases.
- A halogen
Element “b” is halogen because it is in Group VIIA. Group VIIA elements are known as halogens.
17. Argue in what region of the periodic table you will find elements with relatively
a. high ionization energies
Group VIIIA elements have highest ionization energies. Group VIIIA elements are known as noble gases. Noble gases have the highest ionization energies due to their complete outermost electron shells.
b. low ionization energies
Group IA elements have low ionization energies. Group IA elements are known as alkali metals. Alkali metals have low ionization energies due to their larger atomic size and the presence of a single valence electron in their outermost shell.
