PARAMOUNT SCHOOL SYSTEM
Subject: Chemistry – I
Unit 6: Stoichiometry
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 6.1
Write the empirical formulas for the compound containing carbon to hydrogen in the following ratios.
- 1 : 4 CH4
- 2 : 6 CH3
- 2 : 2 CH
- 6 : 6 CH
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 6.2
1. Aspirin is used as a mild pain killer. There are nine carbon atoms, eight hydrogen atoms and four oxygen atoms, in this compound. Write its empirical and molecular formulas.
Molecular formula of Aspirin is C9H8O4
The empirical formula is the simplest whole-number ratio. Therefore, the empirical formula for Aspirin is: C9H8O4
2. Vinegar is 5% acetic acid. This contains 2 carbon atoms, four hydrogen atoms and 2 oxygen atoms. Write its empirical and molecular formulas.
Molecular formula of Vinegar is C2H4O2
The empirical formula is the simplest whole-number ratio. Therefore, the empirical formula for Vinegar is: CH2O
3. Caffeine (C8H10N4O2) is found in tea and coffee. Write the empirical formula for caffeine.
The empirical formula is the simplest whole-number ratio. Therefore, the empirical formula for Caffeine is: C4H5N2O
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 6.3
- Potassium Chlorate (KClO3) is used commonly for the laboratory preparation of oxygen gas. Calculate its formula mass.
Formula mass of KClO3 =39 + 35.5 + 3×16
= 39 + 35.5 + 48
= 122.5 amu
2. When baking soda, NaHCO3 is heated it releases carbon dioxide, which is responsible for the rising of cookies and bread. Determine the formula mass of baking soda and carbon dioxide.
Formula mass of NaHCO3 =23+1+12+3×16
= 23+1+12+48
= 84 amu
Formula mass of CO2 = 12+2×16
= 12+32
= 44 amu
3. Following compounds are used as fertilizers. Determine their formula masses.
(i) Urea, (NH2) 2 CO
Formula mass of (NH2) 2 CO = 2×14 + 2×2 + 12 + 16
= 28 + 4 + 12 + 16
= 60 amu
- Ammonium nitrate, NH4NO3
Formula mass of NH4NO3 = 14 + 1×14 + 14 + 3×16
= 14 + 4 +14 + 48
= 80 amu
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 6.4
1. Calculate the one mole of
(a) Copper
1 mole of Copper (Cu) = 63.5 g
(b) Iodine
Molecular mass of Iodine (I2) = 2×127
1 mole of I2 = 254 g
(c) Potassium
1 mole of K = 39g
(d) Oxygen (O2)
Molecular mass of Oxygen (O2) = 2 x 16
1 mole of O = 32g
2. Differentiate between gram formula mass and gram molecular mass.
| Gram Formula Mass | Gram Molecular Mass |
| Represents one mole of ionic formula units of a compound. | Represents one mole of molecules of a compound or element. |
| Contains 6.022 × 1023 formula units. | Contains 6.022 × 1023 molecules. |
| Used for ionic compounds. | Used for molecular compounds or elements in the molecular state. |
| Example: NaCl | Example: H2O, O2 |
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 6.5
1. The molecular formula of a compound used for bleaching hair is Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2). Calculate:
(a) Mass of this compound that would contain 2.5 moles.
Solution:
Number of moles = 2.5 moles
Molar mass of (H2O2) = 2 x 1 + 2 x 16
= 34g
Mass (in grams) = ?
= 2.5 x 34g
= 85g
(b) Number of moles of this compound that would exactly weight 30 g.
Solution:
Mass of (H2O2) = 30g
Molar mass of (H2O2) = 34g
Number of moles = ?
= 0.88 moles
2. A spoon of table salt NaCl contains 12.5 grams of this salt. Calculate the number of moles it contains.
Solution:
Mass of Sodium Chloride (NaCl) = 12.5g
Molar mass of NaCl = 23+35.5
= 58.5g
Number of moles = ?
= 0.21 moles
3. Before the digestive systems x-rayed, people are required to swallow suspensions of barium sulphate (BaSO4). Calculate mass of one mole of BaSO4 .
Solution:
Molar Mass of BaSO4 = 137+32+4×16
= 137+32+64
= 233g
Therefore,
Mass of 1 mole of BaSO4 = 233g
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 6.6
- Aspirin is compound that contains carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. It is used as a painkiller. An aspirin tablet contains 1.25 x 1030 molecules. How many moles of this compound are present in the tablet?
Solution:
Number of molecules = 1.25×1030 molecules
Avogadro’s number = NA = 6.022×1023
Number of moles = ?
= 2.076 x 106 moles
- A method used to prevent rusting in ships and underground pipelines involves connecting the iron to a block of a more active metal such as magnesium. This method is called cathodic protection. How many moles of magnesium are present in 1 billion (1 x 109) atoms of magnesium.
Solution:
Number of atoms = 1×109 atoms
Avogadro’s number = NA = 6.022×1023
Number of moles = ?
= 1.66 x10-15 moles
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 6.7
Represent the following chemical reactions by chemical equations.
1. Burning of hydrogen (H₂) to produce water.
Hydrogen gas + Oxygen → Water
H2 + O2 → H2O
2. Burning of magnesium (Mg) to produce magnesium oxide (MgO).
Magnesium metal + Oxygen → Magnesium Oxide
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 6.8
Transform the following chemical equations into ionic equations.
1. AgNO₃ + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO₃
Write the substances that are soluble in water in their dissociated form. AgCl (silver chloride) is insoluble in water and precipitates out.
Ag⁺ + NO₃⁻ + Na⁺ + Cl⁻ → AgCl + Na⁺ + NO₃⁻
Remove common ions from both sides,
Ag⁺ + Cl⁻ → AgCl
2. Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl₂ + H₂
Write the substances that are soluble in water in their dissociated form.
Zn + 2H+ + 2Cl− → Zn+2 + 2Cl− + H2
Remove common ions from both sides,
Zn + 2H+ → Zn+2 + H2
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 6.9
Write the molecular formulae of the following compounds.
1. CH3—CH2— OH
C2H6O
2. CH3 — CH2— NH2
C2H7N
3. CH3 – CO – CH3
C3H6O
REVIEW QUESTIONS
1. Encircle the correct answer.
- What is the formula mass of CuSO4.5H2O. (Atomic masses: Cu-3.5, S=32, H= 1)
a. 159.5 b. 185.5 c. 249.5 d. 149.5
- A compound with chemical formula Na2CX3 has formula mass 106amu: Atomic mass of the element X is:
a. 106 b. 23 c. 12 d. 16
- How many moles of molecules are there in 16g oxygen?
a. 1 b. 0.5 c. 0.1 d. 0.05
- What is the mass of 4 moles of hydrogen gas?
a. 8.064g b. 4.032g c. 1g d.1.008g
- What is the mass of carbon present in 44g of carbon dioxide?
a. 12g b. 6g c. 24g d. 44g
- Which term is the same for one mole of oxygen and one mole of water?
a. volume b. mass c. atoms d. molecules
- If one mole of carbon contains x atoms, what is the number of atoms contained in 12g of Mg.
a. x b. 0.5x c. 2x d. 1.5x
2. Give short answer.
i. What is mole?
A mole is an amount of a substance that contains 6.022×1023 particles of that substance. This experimentally determined number is known as Avogadro’s number. It is represented by NA.
ii. Differentiate between empirical formula and molecular formula.
| Empirical Formula | Molecular Formula |
| Which gives the simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element of a compound | Which shows the actual number of atoms of each element present in a compound. |
| It does not show the structure of compound | It shows the structure of compound |
| Two or more compounds can have same empirical formula | Two or more compounds cannot have same molecular formula. |
| Example:CH2O, CH are empirical formula of glucose and benzene | Example: C6H12O6, C6 H6 are molecular formula of glucose and benzene |
iii. What is the number of molecules in 9.0g of steam?
Solution:
Mass in grams = 9.0g
Molar mass of steam (H2O) = 2 x 1 + 16 = 18g
Avogadro’s number = NA = 6.022×1023
Number of molecules = ?
= 6.022×1023
= 0.5 x 6.022 x 1023
= 3.011 x 1023 Molecules
iv. What are the molar masses of Uranium-238 and
Uranium-235?
Molar mass = Atomic mass
Molar mass of uranium-238 = 238g
Molar mass of uranium-235 = 235g
v. Why one mole of hydrogen molecules and one mole of H atoms have different mases?
One mole of hydrogen molecule (H2) contains two hydrogen atoms, its molar mass is 1×2=2g. One mole of H-atom contains only one hydrogen atom, its molar mass is 1×1=1g. That’s why one mole of hydrogen molecules and one mole of H-atoms have different masses.
3. Define:
Ion:
Ion is a charged specie formed from an atom or chemically bonded group of atoms by adding or removing electrons.
Ion may have positive or negative charge.
Molecular Ion:
When a molecule losses or gains electrons, the resulting species is called molecular ion. These are short lived species and only exist at high temperature. Molecular ions do not form ionic compounds.
Formula Unit:
The simplest unit which represents an ionic compound is called formula unit.
Free radical:
Free radical is an atom or group of atoms that contains an unpaired electron. Free radical bear no charge
Example ,
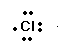
Atomic number:
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is known as atomic number.
Mass number:
The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom is known as its mass number.
Atomic mass unit:
One atomic mass unit (amu) is defined as a mass exactly equal to one twelfth the mass of one C-12 atom.
Mass of one C-12 atom = 12 amu
4. Describe how Avogadro’s number is related to a mole of any substance.
Avogadro’s number is related to a mole of any substance by a relation.
5. Calculate the number of moles of each substance in samples with the following masses.
(a) 2.4g of He:
Mass of Helium (He) = 2.4g
Molar mass of Helium(He)= 4g
= 0.6 moles
(b) 250 mg of Carbon:
Mass of carbon (C) = 250mg = 250g/1000= 0.25g
Molar mass of carbon = 12g
= 0.021 moles
(c) 15g of sodium chloride:
Mass of sodium chloride (NaCl) = 15g
Molar mass of Sodium Chloride = 23 + 35.5 = 58.5g
= 0.256 moles
(d) 40 g of Sulphur:
Mass of Sulphur (S) = 40 g
Molar mass of Sulphur = 32g
= 1.25 moles
(e) 1.5 kg of MgO: (1kg = 1000 g)
Mass of MgO = 1.5 Kg = 1.5 x 1000 = 1500 g
Molar mass of MgO = 24 + 16 = 40g
= 37.5 moles
6. Calculate the mass in grams of each of the following samples:
(a) 1.2 moles of K
Number of moles of Potassium (K) = 1.2 moles
Molar mass of Potassium = 39g
Mass in gram =Number of moles × Molar mass
Mass in grams = 1.2 x 39 = 46.8 g
(b) 75 moles of H2
Number of moles of hydrogen(H2) = 75 moles
Molar mass of hydrogen(H2) = 2 x 1 = 2g
Mass in gram =Number of moles × Molar mass
Mass in grams = 75 x 2 = 150g
(c) 0.25 moles of steam
Number of moles of steam (H2O) = 0.25 moles
Molar mass of steam (H2O) = 2 x 1+16 = 18g
Mass in gram = Number of moles × Molar mass
Mass in grams = 0.25 x 18 = 4.5g
(d) 1.05 moles of CuSO4.5H2O
Number of moles of Copper Sulphate Penta Hydrate= 1.05 moles
Molar mass of CuSo4 .5H2O = 63.5+32+4×16+5(2×1+16)
= 63.5 +32 +64 +5(18)
= 249.5g
Mass in gram =Number of moles × Molar mass
Mass in grams = 1.05 x 249.5 = 261.96g
(e) 0.15 moles of H2SO4
Number of moles of Sulphuric Acid (H2SO4) = 0.15 moles
Molar mass of H2SO4 = 2 x 1 + 32 + 4×16 = 98g
Mass in gram =Number of moles × Molar mass
Mass in grams = 0.15 x 98 = 14.7g
7. Calculate the number of molecules present in each of the following samples
(a) Number of moles = 2.5 moles
Avogadro’s number = NA = 6.022×1023
Number of molecules = ?
Number of molecules = Number of Moles x NA
Number of molecules = 2.5 x 6.022 x 1023
= 1.505 x 1024 molecules
(b) 3.4 moles of ammonia, NH3
Number of moles = 3.4 moles
Avogadro’s number = NA = 6.022×1023
Number of molecules = ?
Number of molecules = Number of Moles x NA
Number of molecules = 3.4 x 6.022 x 1023
= 2.05 x 1024 molecules
(c) 1.09 moles of benzene, C6H6
Number of moles = 1.09 moles
Avogadro’s number = NA = 6.022×1023
Number of molecules = ?
Number of molecules = Number of Moles x NA
Number of molecules = 1.09 x 6.022 x 1023
= 6.56 x 1023 molecules
(d) 0.01 moles of acetic acid, CH3COOH
Number of moles = 0.01 moles
Avogadro’s number = NA = 6.022×1023
Number of molecules = ?
Number of molecules = Number of Moles x NA
Number of molecules = 0.01 x 6.022 x 1023
= 6.02 x 1021 molecules
8. Decide whether or not each of the following is an example of empirical formula
(a) Al2 Cl6
This formula is not in its simplest form, so this is not an empirical formula.
(b) Hg2 Cl2
This formula is not in its simplest form, so this is not an empirical formula.
(c) NaCl
This formula is in its simplest form, so this is an empirical formula.
(d) C2H6O
This formula is in its simplest form, so this is an empirical formula.
9. TNT or trinitrotoluene is an explosive compound used in bombs. It contains 7 C-atoms, 6 H-atoms, 5 N-atoms and 6-O atoms. Write its empirical formula
There are:
- 7 carbon (C) atoms
- 6 hydrogen (H) atoms
- 5 nitrogen (N) atoms
- 6 oxygen (O) atoms
The empirical formula is the simplest whole-number ratio. Therefore, the empirical formula for trinitrotoluene (TNT) is: C7 H6 N5 O6
10. A molecule contains four Phosphorus atoms and ten Oxygen atoms. Write the empirical formula of this compound. Also determine the molar mass of this molecule
There are:
- 4 phosphorus (P) atoms
- 10 oxygen (O) atoms
Molecular formula = P4O10
Molar mass of P4O10 = 4×31 + 10×16
= 124 + 160 = 284g
The empirical formula is the simplest whole-number ratio. Therefore, the empirical formula is: P2O5
11. Indigo (C16H10N2O2) the dye used to colour blue jeans is derived from a compound known as indoxyl (C8H7ON). Calculate the molar masses of these compounds. Also write their empirical formulas
Indigo (C16H10N2O2)
Molar mass = 16×12 + 10 x 1 + 2×14 + 2×16
= 192 + 10 + 28 + 32
= 262g
The empirical formula is the simplest whole-number ratio. Therefore, the empirical formula is: C8H5NO
Indoxyl (C8H7ON)
Molar mass = 8 x12 + 7×1 + 16 + 14
= 96 + 7 + 16 + 14
= 133g
The empirical formula is the simplest whole-number ratio. Therefore, the empirical formula is: C8H7ON
12. Identify the substance that has formula mass of 133.5 amu
(a) MgCl2
Formula mass = 24 + 2×35.5
= 24 + 71
= 95 amu
(b) S2Cl2
Formula mass = 2×32 + 2×35.5
= 64 + 71
= 135 amu
(c) BCl3
Formula mass = 11 + 3×35.5
= 11 + 106.5
= 117.5 amu
(d) AlCl3
Formula mass = 27 + 3×35.5
= 27 + 106.5
= 133.5 amu
The substance with a formula mass of 133.5amu is AlCl₃
13. Calculate the number of atoms in each of the following samples.
(a) 3.4 moles of nitrogen atoms
Number of moles = 3.4 moles
Number of atoms = No. of moles x NA
= 3.4 x 6.022×1023
= 2.05 x 1024 atoms
(b) 23g of Na
Mass in grams = 23 g
Molar mass of Sodium (Na) = 23 g
= 6.022×1023
= 6.022 x 1023
(c) 5 g of H atoms
Mass in grams = 5g
Molar mass of hydrogen(H)= 1g
= 6.022×1023
= 3.01 x 1024 atoms
14. Calculate the mass of the following
(a) 3.24 x 1018 atoms of iron
Number of atoms = 3.24 x 1018 atoms
= 3.01 x 10-4 g
(b) 2 x 1010 molecules of nitrogen gas
Number of molecules = 2 x 1010 molecules
Molar mass of nitrogen gas (N2) = 2 x 14 = 28g
= 9.3 x 10-13 g
(c) 1 x 10 25 molecules water
Number of molecules = 1 x 1025 atoms
Molar mass of water (H2O)= 1×2 + 16 = 18g
= 2.99 x 102g
(d) 3 x 106 atoms of Al
Number of atoms = 3 x 106 atoms
Molar mass of Aluminum(Al)= 27 g
= 1.346 x 10-16g
15. Balance the following chemical equations.
a. Na (s) + H₂O (l) → NaOH (aq) + H₂ (g)
Balanced equation:
2Na (s) + 2 H₂O (l) → 2 NaOH (aq) + H₂ (g)
b. NH₃ → N₂ + H₂
Balanced equation:
2NH₃ → N₂ + 3 H₂
16. Potassium is Group 1 element. It is silvery white metal. It burns in air and forms both potassium oxide and potassium nitride. The nitride ion is N3-.
(a) Predict the formula of potassium oxide and potassium nitride.
Potassium oxide (K₂O): Potassium (K) has a +1 charge, and oxygen (O) has a -2 charge. To balance the charges, the formula is K₂O.
Potassium nitride (K₃N): Potassium (K) has a +1 charge, and the nitride ion (N³⁻) has a -3 charge. To balance the charges, the formula is K₃N.
(b) A 0.5g sample of K was added in 100cm3 of water.
K (s) + H2O (l) → KOH (aq) + H2(g)
Show that 1.28 x10-2 mole of K were added to the water.
Mass of K = 0.5 g
Molar mass of K = 39 g/mol
= 1.28 x10-2 mole
(c) Balance above chemical equation.
2K (s) + 2H2O (l) → 2KOH (aq) + H2(g)
(d) Transform above chemical equation into ionic equation.
Write the substances that are soluble in water in their dissociated form
K (s) + H₂O (l) → K⁺ (aq) + OH⁻ (aq) + H₂ (g)
(e) Calculate the number of atoms present in the sample of K.
Number of moles of K = 1.28×10−2moles
Avogadro’s number NA = 6.022×1023
Number of atoms = No. of moles x NA
= 1.28×10−2 x 6.022×1023
= 7.7 × 1021 atoms
(f) Predict period number of potassium in the periodic table.
Potassium (K) is in Period 4 of the periodic table.
