PARAMOUNT SCHOOL SYSTEM
Subject: Chemistry – I
Unit 8: Energetics
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 8.1
Classify the following processes as exothermic or endothermic.
(a) Freezing of water
Exothermic: Freezing releases heat to the surroundings as water changes from liquid to solid.
(b) Combustion of methane
Exothermic: Combustion releases energy in the form of heat and light.
(c) Sublimation of dry ice
Endothermic: Sublimation absorbs heat as dry ice changes directly from solid to gas.
(d) H₂O (l) → H₂O (g)
Endothermic: This is the process of vaporization, which requires heat to convert liquid water to vapor.
(e) decomposition of limestone.
Endothermic: Decomposition absorbs heat to break down calcium carbonate into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
CONCEPT ASSESSMENT EXERCISE 8.2
Calculate the enthalpy of the following reaction from the given bond energy data. Bond energy of H-H, F-F, H-F bonds are 436kJ/mol, 155kJ/mol and 567kJ/mol respectively.
Balanced Chemical Equation:
H2(g)+F2(g) → 2HF(g)
ΔHo = ?
Bond Energy of H-H = 436kJ/mol
Bond Energy of F-F = 155kJ/mol
Bond Energy of H-F = 567kJ/mol
Sum of Bond dissociation energies of reactants=436+155=591kJ/mol
Sum of Bond dissociation energies of products = 2×567=1134kJ/mol
ΔH∘= Sum of Bond dissociation energies of reactants− Sum of Bond energies of products
=591kJ/mol−1134kJ/mol
= − 543kJ/mol
REVIEW QUESTIONS
1. Encircle the correct answer.
- If the ΔH value is negative, then the reaction will be.
(a) Exothermic (b) Endothermic
(c) May or may not be Exothermic or Endothermic (d) None of these
- All chemical reactions involve.
(a) Catalysts (b) Enzymes (c) Energy changes (d) All of these
- Which is not released in aerobic respiration?
(a) Carbon dioxide (b) Water (c) Energy (d) Lactic acid
- A catalyst increases the rate of a chemical reaction by.
(a) Increasing activation energy (b) Increasing the enthalpy of reaction
(c) Decreasing the enthalpy of reaction (d) None of these
- Activation energy of a chemical reaction must be energy of reacting molecules the average kinetic.
(a) Lower than (b) Greater than (c) Equal to (d) None of these
2. Give short answer.
- Define exothermic and endothermic reactions.
Exothermic Reactions: A chemical reaction that proceeds with the evolution of heat is called an exothermic reaction. In an exothermic reaction, the chemical system transfers energy to the surroundings as the reactants are converted to products.
Example: Burning of fuels.
Endothermic Reactions: A chemical reaction that proceeds with the absorption of heat is called an endothermic reaction. In these reactions, heat is transferred from the surroundings to the system.
Example: Sublimation of dry ice.
- Define enthalpy of a chemical reaction.
The enthalpy of reaction is the amount of heat or thermal energy evolved or absorbed during a chemical reaction. It reflects the change in the heat content of the system as reactants are converted into products.
- The enthalpy change (ΔHo) is negative, when reaction is Exothermic
- The enthalpy change (ΔHo) is positive, when reaction is Endothermic
- What is anaerobic respiration?
Anaerobic respiration: Respiration that does not require oxygen to break down glucose to release energy is called anaerobic respiration.
Glucose → Lactic acid + Energy
Anaerobic respiration releases less energy than aerobic respiration.
- Define activation energy.
Activation energy is the minimum energy required for particles to collide effectively and react. It must overcome electron repulsion and ensure correct orientation. If particles lack this energy, no reaction occurs. Higher activation energy means a slower reaction rate, while lower activation energy speeds up the reaction.
- What is the role of a catalyst in a chemical reaction.
A catalyst speeds up a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy needed. It remains unchanged after the reaction and does not affect the overall energy change. This allows reactions to happen faster and more efficiently, even at lower temperatures. Enzymes are biological catalysts in living organisms.
- Differentiate between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
| Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration |
| Requires oxygen to break down glucose. | Does not require oxygen; breaks down glucose without it. |
| Produces carbon dioxide, water, and energy. | Produces lactic acid and energy. |
| Releases more energy because it fully oxidizes glucose. | Releases less energy as glucose is only partially broken down. |
| Primarily uses glucose for energy. | Relies on lipids for additional energy when glucose is insufficient. |
3. How can you determine the enthalpy of a chemical reaction?
First write balanced chemical reaction in gaseous state and apply the formula.
ΔH = Sum of bond dissociation energies of reactants − Sum of bond energies of products.
4. Explain, how does the process of respiration provides us energy?
Respiration provides energy by oxidizing glucose in the body, releasing energy through an exothermic reaction. There are two types of respiration processes.
- Aerobic Respiration: This process requires oxygen and breaks down glucose into carbon dioxide and water, releasing a significant amount of energy.
- Anaerobic Respiration: This process occurs without oxygen, breaking down glucose into lactic acid and releasing less energy.
When glucose oxidation is insufficient, lipids are oxidized to provide additional energy.
5. Draw labeled reaction pathway diagram for an exothermic and an endothermic reaction.
Exothermic Reaction:
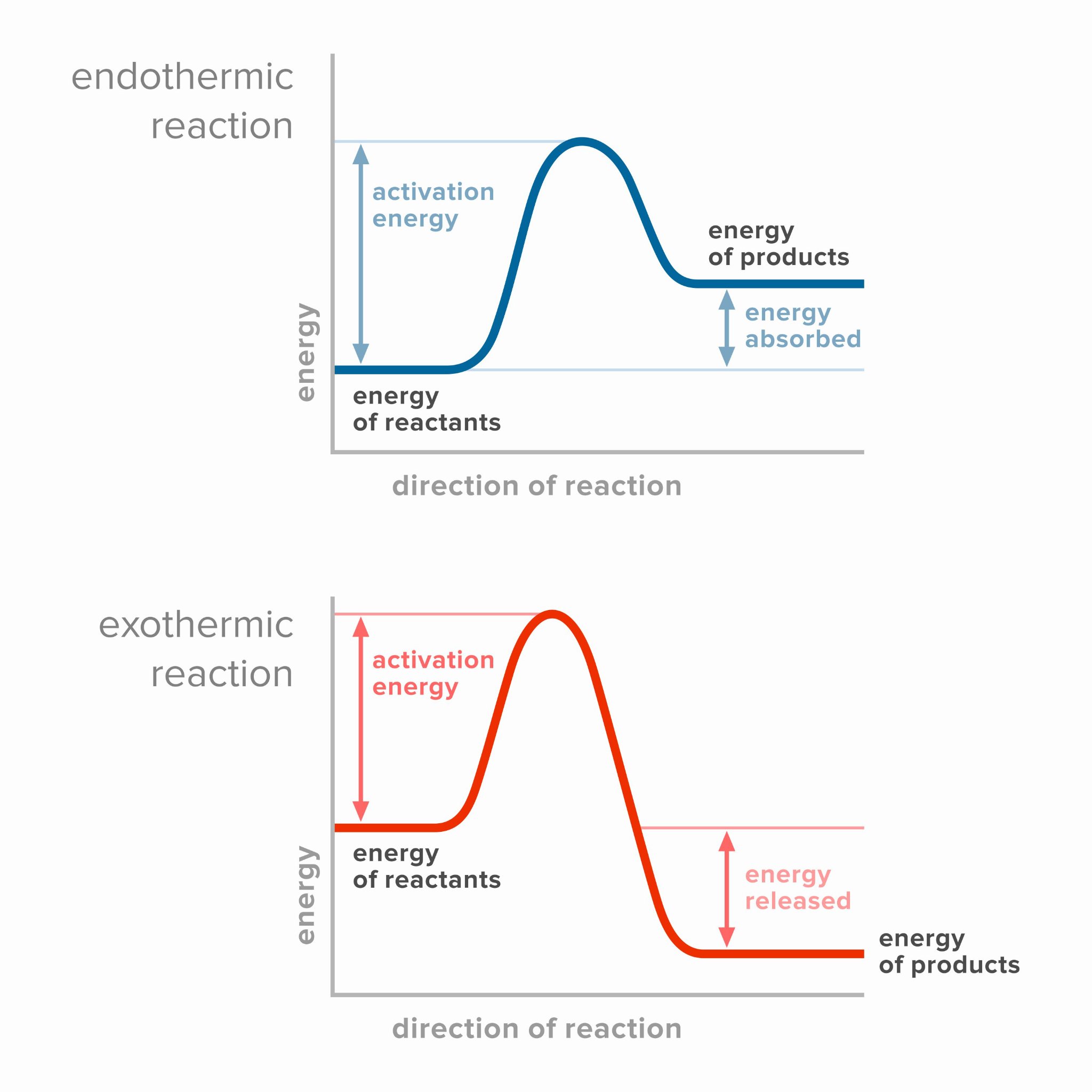
Endothermic Reaction:

6. Calculate the enthalpy of reaction between hydrogen and chlorine to form hydrogen chloride from the given bond energy data. Bond energy of H-H, CI-CI, H-Cl are 436kJ/mol, 243kJ/mol and 432kJ/mol respectively.
Balanced Chemical Equation:
H2(g)+Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g)
ΔHo = ?
Bond Energy of H-H = 436kJ/mol
Bond Energy of Cl-Cl = 243kJ/mol
Bond Energy of H-Cl = 432kJ/mol
Sum of Bond dissociation energies of reactants=436+243 = 679kJ/mol
Sum of Bond dissociation energies of products = 2×432 = 864kJ/mol
ΔH∘= Sum of Bond dissociation energies of reactants− Sum of Bond energies of products
= 679 kJ/mol − 864 kJ/mol
ΔH∘ = − 185 kJ/mol
7. Justify the statement that the process of respiration is crucial for us.
Respiration is crucial for us because it releases energy from glucose, which is essential for all bodily functions. This biochemical process, particularly aerobic respiration, efficiently provides the energy required for growth, repair, and maintenance of cells, supporting overall health and survival.
